NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED
WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this
URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Copyright © 2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

ii
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
CONTENTS
Preface v
Overview v
Organization v
Obtaining Documentation and Support v
CHAPTER
1 Getting Started 1-1
Overview 1-1
Physical Description 1-2
Power Adapters 1-4
Hardware Installation 1-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera Hardware Installation 1-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera Hardware Installation 1-8
LED Definitions 1-15
Hardware Reset 1-15
MicroSD/SDHC/SDXC Card Capacity 1-15
Network Deployment 1-15
General Connection (PoE) 1-16
Network Connection 1-16
Auto Focus 1-18
CHAPTER
2 Accessing the IP Camera 2-1
Using Web Browsers 2-1
Performing the Initial Setup of the IP Camera 2-2
Using RTSP Players 2-3
Using 3GPP-Compatible Mobile Devices 2-3
CHAPTER
3 IP Camera Main Page 3-1
Live Video Window for H.264 or H.265 Video Streams 3-3
Live Video Window for MJPEG Video Streams 3-5
CHAPTER
4 Client Settings 4-1
H.265/H.264 Media Options 4-1
H.265/H.264 Protocol Options 4-1

Contents
iii
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Two Way Audio 4-2
MP4 Saving Options 4-2
Local Streaming Buffer Time 4-2
Joystick settings 4-2
CHAPTER
5 Configuration 5-1
Accessing the Settings Pages 5-2
System > General settings 5-3
System > Homepage layout 5-3
General settings 5-3
Theme Options 5-4
System > Logs 5-5
Log server settings 5-5
System log 5-5
Access log 5-6
System > Parameters 5-6
System > Maintenance 5-6
General settings > Upgrade firmware 5-6
General settings > Reboot 5-7
General settings > Restore 5-7
Import/Export files 5-7
Media > Image 5-8
General settings 5-8
Day/Night settings 5-9
Image settings 5-9
Exposure 5-10
Lens configuration 5-12
Focus 5-12
Focus Window 5-13
Privacy Mask 5-13
Media > Video 5-14
Stream settings—Mode - Resolution and Frame rate 5-14
Media > Audio 5-19
Network > General settings 5-19
Network Type Tab 5-19
Network > Streaming protocols 5-21
HTTP streaming 5-21
RTSP Streaming 5-22

Contents
iv
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Network > QoS (Quality of Service) 5-24
Requirements for QoS 5-24
QoS models 5-24
Network > SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) 5-25
SNMP Configuration 5-25
Security > User accounts 5-25
Privilege Management 5-26
Account Management 5-26
Security > HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL) 5-26
Create and Install Certificate Method 5-26
Security > Access List 5-27
General Settings 5-27
Filter 5-28
Administrator IP address 5-29
Security > IEEE 802.1X 5-29
Security > SSH 5-30
PTZ > PTZ settings 5-30
Digital PTZ Operation (E-PTZ Operation) 5-30
Patrol Settings 5-31
Event > Event settings 5-31
Event 5-31
Add server 5-33
Action 5-34
Add media 5-35
Customized Script 5-37
Applications > Motion detection 5-37
How does Motion Detection Work? 5-38
Applications > DI and DO 5-38
Applications > Tampering detection 5-38
Applications > Audio detection 5-39
Applications > Package management 5-41
Application > PIR 5-41
Recording > Recording settings 5-42
Recording Settings 5-42
Local storage > SD card management 5-44
SD card status 5-44
SD card format 5-44
SD card control 5-44

v
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Preface
Overview
This document provides information about installing deploying, and using the Cisco Video Surveillance
8020 IP Camera and the 8030 IP Camera.
Organization
This manual is organized as follows:
Obtaining Documentation and Support
For information about obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation. This document also lists
new and revised Cisco technical documentation. It is available at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
Chapter 1, “Getting Started” Provides information about getting started with
and understanding the IP Camera
Chapter 2, “Accessing the IP Camera” Explains how to access the IP camera through web
browsers and RTSP players
Chapter 3, “IP Camera Main Page” Describes the layout of the main page of the IP
camera web based interface
Chapter 4, “Client Settings” explains how to select the stream transmission
mode and saving options on the local computer
Chapter 5, “Configuration” Describes the IP camera settings options

vi
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Preface
Obtaining Documentation and Support

CHAPTER
1-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
1
Getting Started
This chapter provides information about getting started with and understanding the IP camera. It
includes the following sections:
• Overview, page 1-1
• Physical Description, page 1-2
• Power Adapters, page 1-4
• Hardware Installation, page 1-4
• LED Definitions, page 1-15
• Hardware Reset, page 1-15
• MicroSD/SDHC/SDXC Card Capacity, page 1-15
• Network Deployment, page 1-15
• Auto Focus, page 1-18
Overview
The Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 (indoor) and 8030 (indoor/outdoor) IP Cameras are high-definition,
full-functioned video endpoints with industry-leading image quality and processing power. The cameras
are capable of 5MP resolution at 30 frames per second (fps) while optimizing network usage with H.264,
H.265, or MJPEG compression. Contact closures and two-way audio allow integration with
microphones, speakers, and access control systems. With their open, standards-based design, the
cameras provide ideal platforms for integration and operation as independent devices or as part of a
Cisco video surveillance network.
Key features and benefits of the Cisco Video Surveillance cameras include:
• True high-definition video—The cameras stream crisp and clear 5MP video at 30 fps while
maintaining low network bandwidth.
• Streaming—The cameras can stream H.264, H.265, and MJPEG video simultaneously. Each video
stream can be configured with individual resolution, quality, and frame-rate settings.
• Day/night operation—The cameras provide true day/night functionality, and include an infrared (IR)
filter that automatically switches to night mode in low-light scenes. This function can be set to
manual, automatic, or scheduled control.
• Flexible power option—The cameras support Power over Ethernet (PoE) 802.3af Class 0 for 8020
models, 802.3at Class 4 for 8030 models, and 12 VDC for both models.

1-2
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Physical Description
• Mounting options—The cameras can be installed to either a ceiling or wall.
• Motion Detection and Event notification—The cameras can examine designated areas for activity
and notify users or other applications when they detect activity that exceeds a predefined sensitivity
and threshold. The cameras also provide one digital input and one digital output that can be used to
initiate specific actions when an alarm is detected.
Physical Description
The following figures illustrate the camera:
• Figure 1-1—Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera inner view
• Figure 1-2 —Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera outer view
• Figure 1-3 —Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera physical view
Figure 1-1 Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera Inner View
1 Reset button
2 RJ45 Ethernet port
3 IR LEDs
4 Motorized or fixed lens
5 PIR
6 Microphone
7 SD/SDHC/SDXC Card Slot
8 Terminal block

1-3
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Physical Description
Figure 1-2 Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera Outer View
Figure 1-3 Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera Physical View
1 Microphone
2 PIR

1-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Power Adapters
Power Adapters
Hardware Installation
The following sections describe how to install your camera:
• Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera Hardware Installation, page 1-4
• Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera Hardware Installation, page 1-8
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera Hardware Installation
To perform the hardware installation of the Cisco Video Surveillance 8020 IP Camera, follow these
steps:
Step 1 Make a note of the MAC address of the camera.
The MAC address is printed on the label that is attached to the camera.
Step 2 Remove the dome cover by pressing the release button.
1 IR LEDs
2 Motorized or fixed lens
3 SD/SDHC/SDXC card slot
4 Terminal block
5 Reset button
6 DI/DO wire inlet
7 Ethernet cable inlet
8 RJ45 Ethernet port
Figure 1-4 Power Adapters
CIVS-IPC-8020 This product is intended to be supplied by a Listed Power Adapter with LPS, rated PoE
36-57Vdc, 0.7A-0.44A; 12Vdc, 1.75A min. (for model CIVS-IPC-8030); rated PoE
36-57Vdc, 0.4A-0.28A; 12Vdc, 1.0A min. (for model CIVS-IPC-8020)
CIVS-IPC-8020-S
CIVS-IPC-8030
CIVS-IPC-8030-S

1-5
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 3 The camera comes with a PIR sensor. Plan your installation position so that the PIR can cover the area
of your interest where the intrusion may occur. The rated detection distance is 5 meters.
Step 4 Attach the alignment sticker to a preferred location. Drill holes on the wall or ceiling to install the plastic
anchor and secure the camera using the included screws.
If preferred, drill one routing hole.

1-6
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 5 If applicable, connect DI/DO wires, 12V DC power, or audio wires to the terminal block.

1-7
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Here is the DI/DO Diagram:
• The DO+ pin provides 5V output voltage, and the max. load is 50mA.
• The max. voltage for DO- pins is 80VDC (External power). In order to control AC devices, the above
diagram can be taken in consideration. The diagram uses a relay to control the ON/OFF condition
of the AC device.
• An external relay can be triggered by using DO+ or by an external power source, depending on the
type of relay you use.
• In case of using an individual relay (instead of using a relay module), for protection against voltage
or current spikes, a transient voltage suppression diode must be connected in parallel with the
inductive load.
Step 6 Adjust the shooting direction by turning and orienting the lens module. Use a Phillips screwdriver to
loosen the retention screws on the sides.

1-8
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 7 Adjust the shooting direction by turning and orienting the lens module. Use a Phillips screwdriver to
loosen the retention screws on the sides.
Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera Hardware Installation
To perform the hardware installation of the Cisco Video Surveillance 8030 IP Camera, follow these
steps:
Step 1 Make a note of the MAC address of the camera.
The MAC address is printed on the label that is attached to the camera.
Step 2 Use the included T8 wrench to remove the dome cover. If local recording is preferred, install an SD card.

1-9
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 3 Loosen and remove the waterproof connectors.
Step 4 Insert an Ethernet cable through the cable gland, and the rubber seal.
Step 5 Remove part of cable sheath.
Step 6 You will need an RJ45 crimping tool to attach the Ethernet wires to a connector. When done, connect the
cable to the camera’s Ethernet RJ45 socket.
Step 7 If applicable, connect DI/DO wires, 12V DC power, or audio wires to the terminal block.

1-10
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Here is the DI/DO Diagram:

1-11
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
• The DO+ pin provides 5V output voltage, and the max. load is 50mA.
• The max. voltage for DO- pins is 80VDC (External power). In order to control AC devices, the above
diagram can be taken in consideration. The diagram uses a relay to control the ON/OFF condition
of the AC device.
• An external relay can be triggered by using DO+ or by an external power source, depending on the
type of relay you use.
• In case of using an individual relay (instead of using a relay module), for protection against voltage
or current spikes, a transient voltage suppression diode must be connected in parallel with the
inductive load.
Step 8 Attach the included alignment sticker to a preferred location. Drill holes for mounting screws and if
preferred, drill one or two routing holes.
Step 9 When fastening the screws, do not completely tighten the screws. Pass cables through the routing holes,
and then mount the camera by passing the screw heads through the keyhole slots. Turn the camera
counter-clock wise, and then fasten the screws.

1-12
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 10 If you do not need to route your cables through the side opening, you can use the double-sided tape to
attach a plastic stopper to the opening on the side of the camera.

1-13
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Avoid using a conduit with a hex nut larger than 35mm.
Step 11 With a live view displayed on your laptop, adjust the zoom and focus to obtain an optimal image. Check
the live view to ensure the image is in focus.
Step 12 Replace the desiccant bag on the camera.

1-14
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Hardware Installation
Step 13 Align and install the dome cover.
Step 14 With a live view displayed on your laptop, adjust the zoom and focus to obtain an optimal image. Check
the live view to ensure the image is in focus. [Include this step? If yes, do we need to tell users how to
get to this live image?]

1-15
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
LED Definitions
LED Definitions
Table 1-1 describes the LEDs on the Cisco Video Surveillance IP Camera.
Hardware Reset
The recessed button (see Figure 1-1 on page 1-2 for the 8020 or Figure 1-3 on page 1-3 for the 8030) is
used to reset the system or restore the factory default settings. Sometimes resetting the system can return
the camera to normal operation. If the system problems remain after reset, restore the factory settings
and install again.
• Reset—Press the recessed reset button. Wait for the camera to reboot.
• Restore—Press and hold the reset button until the status LED rapidly blinks. All settings will be
restored to factory default. Upon successful restore, the status LED will blink green and red during
normal operation.
MicroSD/SDHC/SDXC Card Capacity
The camera is compliant with SD/SDHC/SDXC 16GB / 8GB / 32GB / 64GB and other preceding
standard SD cards.
Network Deployment
The following sections provide information about deploying the camera on a network:
• General Connection (PoE), page 1-16
• Network Connection, page 1-16
Table 1-1 IP Camera LEDs
Item LED Status Description
1 Steady red Powered and system booting, or network
failed
Red LED off Power off
Green LED off Network disconnected
2 Steady red and green LED blinks every 1
second
Connected to network
3 Green LED blinks every 1 second and red
LED blinks consecutively every 0.15 second
Upgrading firmware
4 Green and red LEDs blink every 0.15 second,
green and red light on, then blink again
Restoring defaults
5 Red LED is on, green LED blinks and red
LED is constantly on
Status after a reset (network connected)
Green and red LEDs are constantly on Status after a reset (network disconnected)

1-16
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Network Deployment
General Connection (PoE)
Using a PoE-Enabled Switch
The camera is PoE-compliant, allowing transmission of power and data via a single Ethernet cable.
Figure 1-5 illustrates how to connect the camera to a PoE-enabled switch via an Ethernet cable.
Figure 1-5 Connecting the Camera to a PoE-Enabled Switch
Using a Non-PoE Switch
Use a PoE power injector (optional) to connect between the camera and a non-PoE switch, as shown in
Figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6 Connecting the Camera to a Non-PoE Switch
Note • The camera is only to be connected to PoE networks without routing to outside plants.
• For a PoE connection, use only UL listed I.T.E. with PoE output.
Network Connection
Internet Connection via a Router
To set up the camera over the Internet, make sure you have a router and follow these steps:
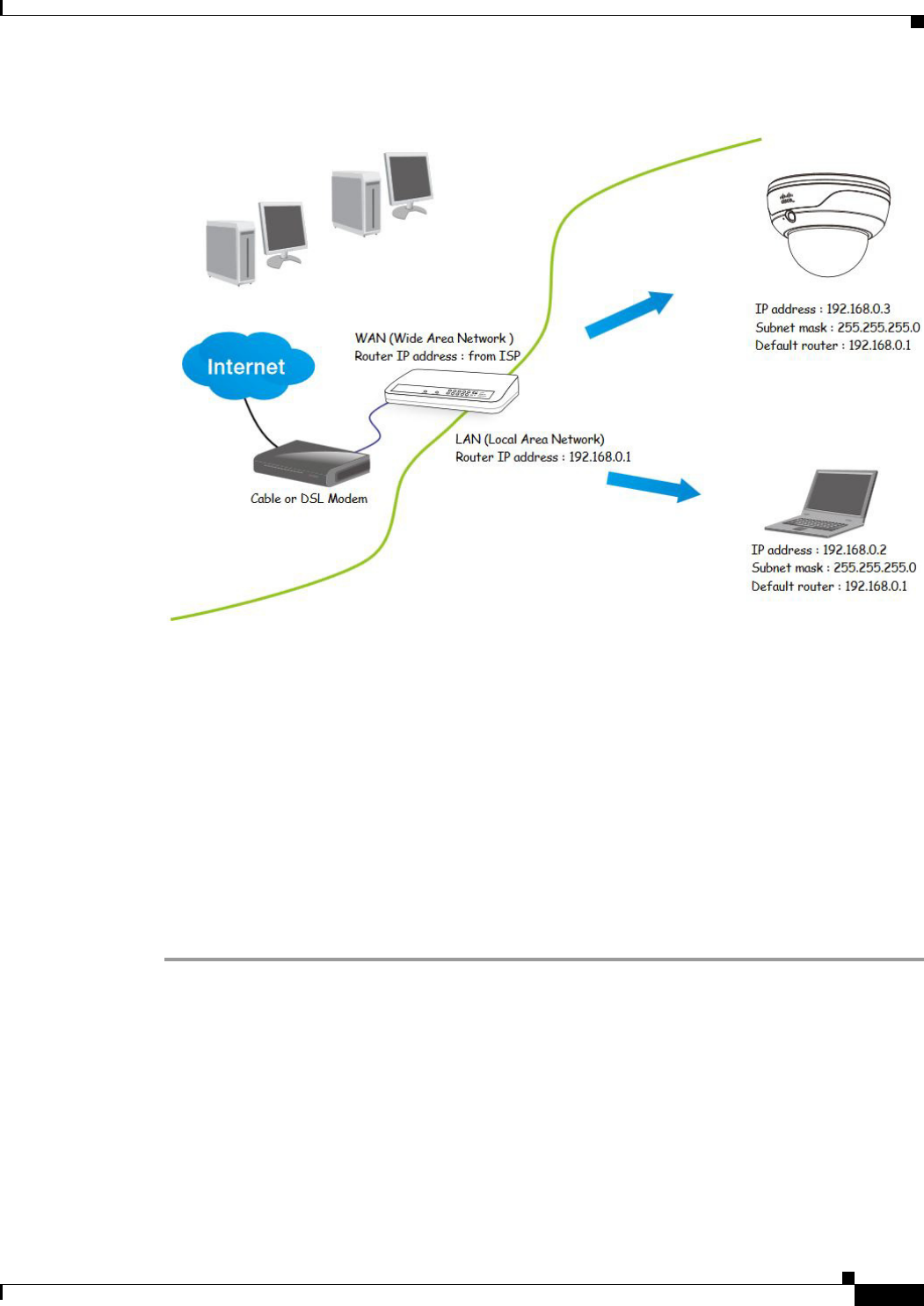
Step 1 Connect your camera behind a router, the Internet environment is illustrated in Figure 1-7.
1-17
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Network Deployment
Figure 1-7 Connecting the Camera Via a Router
Step 2 In this case, if the Local Area Network (LAN) IP address of your camera is 192.168.0.3, forward the
following ports for the camera on the router.:
• HTTP port: default is 80
• RTSP port: default is 554
• RTP port for video: default is 5556
• RTCP port for video: default is 5557
If you have changed the port numbers on the Network page, open the ports accordingly on your router.
For information about how to forward ports on the router, see your router documentation.
Step 3 Find out the public IP address of your router provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Use the public IP and the secondary HTTP port to access the camera from the Internet. See the “Network
> General settings” section on page 5-19 for more information.
Internet Connection with Static IP
Choose this connection type if you are required to use a static IP for the camera. See the “Network >
General settings” section on page 5-19 for more information.
Internet Connection via Point-to-Point over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Choose this connection type if you are connected to the Internet via a DSL Line. See description of
PPPoE (Point-to-point over Ethernet) in the “Network Type Tab” section on page 5-19.

1-18
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Auto Focus
Configure the router, virtual server or firewall, so that the router can forward any data coming into a
preconfigured port number to a camera on the private network, and allow data from the camera to be
transmitted to the outside of the network over the same path.
When properly configured, you can access a camera behind the router using the HTTP request such as:
http://122.146.57.120:8000.
If you change the port numbers on the Network configuration page, open the ports accordingly on your
router. For example, you can open a management session with your router to configure access through
the router to the camera within your local network. See your network administrator for router
configuration if you have troubles with the configuration.
For more information about network configuration options (such as that of streaming ports), choose
Configuration > Network Settings in the IP camera web-based interface. Cisco also provides the
automatic port forwarding feature as an NAT traversal function with the precondition that your router
must support the UPnP port forwarding feature.
Auto Focus
On the web session, choose Configuration > Media > Image > Focus. Perform the Auto Focus function
for best image. However, if you have cascaded cameras, do this one by one. Do not perform this function
simultaneously on multiple cameras because the motorized lens also consume considerable power, and
may cause the last camera on the line to hang.
From Forward to
122.146.57.120:8000 192.168.2.10:80
122.146.57.120:8001 192.168.2.11:80
... ...

CHAPTER
2-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
2
Accessing the IP Camera
This chapter explains how to access the IP camera through web browsers and RTSP players.
This chapter includes these topics:
• Using Web Browsers, page 2-1
• Performing the Initial Setup of the IP Camera, page 2-2
• Using RTSP Players, page 2-3
• Using 3GPP-Compatible Mobile Devices, page 2-3
Using Web Browsers
To access the camera, follow these steps:
Step 1 Launch your web browser (Microsoft Internet Explorer Mozilla Firefox).
Step 2 Enter the IP address of the camera in the address field and then press Enter.
Live video is displayed in your web browser.
If it is the first time installing the camera, a dialog box prompts for information. Follow the instructions
to install the required plug-in on your computer.
Step 3 If you see a dialog box indicating that your security settings prohibit running ActiveX Controls, enable
the ActiveX Controls for your browser:
a. Choose Tools > Internet Options > Security > Custom Level.
b. Look for Download signed ActiveX controls, select Enable or Prompt, and then click OK.
c. Refresh your web browser, then install the ActiveX control. Follow the instructions to complete
installation
Note • The camera utilizes 32-bit ActiveX plugin. You cannot open a management/view session with the
camera using a 64-bit IE browser.
• If you encounter this problem, try execute the Iexplore.exe program from C:\Windows\SysWOW64.
A 32-bit version of IE browser will be installed.

2-2
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 2 Accessing the IP Camera
Performing the Initial Setup of the IP Camera
• On Windows 7, the 32-bit explorer browser can be accessed from here: C:\Program Files
(x86)\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe.
Tip The onscreen Java control can malfunction under the following situations: A PC connects to different
cameras that are using the same IP address (or the same camera running different firmware versions).
Removing your browser cookies will solve this problem.
If you encounter problems with displaying the configuration menus or UI items, try disabling the
Compatibility View on Internet Explorer 8 or 9.
You may also press the F12 key to open the developer tools utility, and then change the Browser Mode
to the genuine Internet Explorer 8 or 9 mode.
In the event of plug-in compatibility issues, you may try to uninstall the plug-in that was previously
installed.
Performing the Initial Setup of the IP Camera
After you install IP camera or after you perform a factory reset procedure, you must access the IP camera
and make initial configuration settings. These settings include root passwords, and whether the IP
camera can be accessed through an HTTPS connection in addition to the default HTTP connection.
By default, when the IP camera powers on, it attempts to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server in
your network. If the camera cannot obtain an IP address through DCHP, an IP address is assigned using
the Link-Local address scheme. The camera acquires an IP address by inserting part of its MAC address
into the 169.254.x.x IP address. To do this, the camera converts the hex digits of the MAC address to
decimal values and then applies them to create an IP address in the following format:
169.254.MAC:9-10.MAC:11-12
where MAC:9-10 are the 9th and 10th digits in the MAC address, and MAC:11-12 are the 11th and 12th
digits.
For example, using this method, camera with a MAC address of 00-11-22-33-44-55 acquires an IP
address of 169.254.68.85, given that hex 44 = 68 decimal and hex 55 = 85 decimal.
To connect to the IP camera for the first time and make initial configuration settings, perform the
following steps:
Step 1 Start Internet Explorer, enter HTTP://ip_address in the address field, and press Enter.
Replace ip_address with the IP address that the IP camera obtained through DHCP or, if the camera was
unable to obtain this IP address, enter 169.254.x.x as obtained by camera.
The Configure password window appears
Step 2 In the Password and Confirm Password fields, enter a password for the IP camera root user.
Step 3 Enable / disable HTTPs check box as required.
Step 4 Click Save.

2-3
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 2 Accessing the IP Camera
Using RTSP Players
Using RTSP Players
To view the streaming media using RTSP players, you can use one of the following players that support
RTSP streaming.
• Quick Time Player
• VLC media player
Step 1 Launch the RTSP player.
Step 2 Choose File > Open URL. A URL dialog box will pop up.
Step 3 The address format is
rtsp://ip_address:rtsp_port/RTSP_streaming_access_name_for_stream1_or_stream2.
As most ISPs and players only allow RTSP streaming through port number 554, set the RTSP port to
554. For more information, see the “RTSP Streaming” section on page 5-22.
Step 4 The live video will be displayed in your player.
For more information about how to configure the RTSP access name, see the “RTSP Streaming” section
on page 5-22.
Using 3GPP-Compatible Mobile Devices
To view the streaming media through 3GPP-compatible mobile devices, make sure the camera can be
accessed over the Internet. For more information on how to set up the camera over the Internet, see the
“Network Deployment” section on page 1-9.
To utilize this feature, do the following on the camera:
Step 1 Because most players on 3GPP mobile phones do not support RTSP authentication, make sure the
authentication mode of RTSP streaming is set to disable. For more information, see the “RTSP
Streaming” section on page 5-22.
Step 2 As the bandwidth on 3G networks is limited, you will not be able to use a large video size. Set the video
streaming parameters as follows. For more information, see the “RTSP Streaming” section on page 5-22.
• Video Mode—H.264
• Frame Size—176 X 144
• Maximum frame rate—5 fps
• Intra frame period—1S
• Video quality (Constant bit rate)—40kbps
Step 3 As most ISPs and players only allow RTSP streaming through port number 554, set the RTSP port to
554. For more information, see the “RTSP Streaming” section on page 5-22.
Step 4 Launch the player, such as QuickTime, on the 3GPP-compatible mobile devices.

2-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 2 Accessing the IP Camera
Using 3GPP-Compatible Mobile Devices
Step 5 Type the following URL commands into the player. The address format is
rtsp://public_ip_address_of_your camera:rtsp_port/
RTSP_streaming_access_name_for_stream_#_with_small_frame_size_and_frame_rate.
For example:
rtsp://192.168.10.15:554/live2.sdp
You can configure Stream #2 into the suggested stream settings as shown above for live viewing on a
mobile device.

CHAPTER
3-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
3
IP Camera Main Page
This chapter explains the layout of the IP camera Main page. It is composed of the following sections:
Cisco Logo, Host Name, Camera Control Area, Configuration Area, Menu, and Live Video Window.
Figure 3-1 illustrates the Main page.

3-2
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
Figure 3-1 Camera Main Page
1 Cisco Logo. Click this logo to visit the Cisco website
2 Resize buttons:
• Click the Auto button, the video cell will resize automatically to fit the monitor
• Click 100% is to display the original homepage size
• Click 50% is to resize the homepage to 50% of its original size
• Click 25% is to resize the homepage to 25% of its original size.
3 Host Name. The host name can be customized to fit your needs. The name can be changed especially there are many
cameras in your surveillance deployment. For more information, see the “System > General settings” section on page 5-3.

3-3
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
Live Video Window for H.264 or H.265 Video Streams
When the video mode is set to H.264 or H.265, the Live Video window appears as shown in Figure 3-2.
For further configuration, see Chapter 4, “Client Settings.”
This window also includes the following:
• PTZ Panel—This camera supports “digital” (e-PTZ) pan/tilt/zoom control, which allows roaming a
smaller view frame within a large view frame. See the “PTZ > PTZ settings” section on page 5-30
for detailed information.
• Global View: Click on this item to display the Global View window. The Global View window
contains a full view image (the largest frame size of the captured video) and a floating frame (the
viewing region of the current video stream). The floating frame allows you to control the e-PTZ
function (Electronic Pan/ Tilt/Zoom). For more information about e-PTZ operation and about how
to set up the viewing region of the current video stream, see the “PTZ > PTZ settings” section on
page 5-30.
Note • The PTZ buttons on the panel are not operational unless you are showing only a portion of the full
image. If the live view window is displaying the full view, the PTZ buttons are not functional.
• For a megapixel camera, it is recommended to use monitors of the 24 inch size or larger, and are
capable of 1600x1200 or better resolutions.
4 Configuration Area:
• Client Settings—Click this button to access the client setting page. For more information, see Chapter 4, “Client
Settings.”
• Configuration—Click this button to access the configuration page of the camera. It is suggested that a password be
applied to the camera so that only the administrator can configure the camera. For more information, see Chapter 5,
“Configuration.”
• Language—Click this button to choose a language for the user interface. You can also change a language on the
Configuration page
5 Video view window. Shows the video stream from the IP camera.
The information in this window depends on the video stream configuration. Depending on the camera model and camera
configuration, some buttons may not be available.
See the “Live Video Window for H.264 or H.265 Video Streams” section on page 3-3 and the “Live Video Window for
MJPEG Video Streams” section on page 3-5.
6 Hide button. You can click the hide button to hide or display the control panel.
7 Camera Control Area:
• Video Stream—This camera supports multiple streams (streams 1 and 2) simultaneously. You can select any of them
for live viewing. For more information about multiple streams, see the “Media > Video” section on page 5-14.
• Manual Trigger—Click to enable/disable an event trigger manually. Configure an event setting on the Application
page before you enable this function. A total of 3 event configuration can be configured. For more information about
event setting, see the “Event > Event settings” section on page 5-31. If you want to hide this item on the Home page,
go to Configuration> System > Homepage Layout > General settings > Customized button to deselect the show
manual trigger button check box.

3-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
• The following are the defaults for audio settings:
- For cameras with built-in microphone: Not Muted.
- For cameras without built-in microphone: Muted.
• To receive audio input from an external microphone, you may need to enable the audio input from
Media > Audio. See the “Media > Audio” section on page 5-19 for more information.
Figure 3-2 Live Video Window for H.264 or H.265
1 Time. Display the current date and time. For more information, see the “Image settings” section
on page 5-9.
2 H.264 or H.265 protocol and media options. The transmission protocol and media options for
H.264 or H.265 video streaming.
3 Video title. The video title can be configured. For more information, see the “Media > Image”
section on page 5-8.
4 Title and Time. Video title and time can be stamped on the streaming video. For more information,
see the “Image settings” section on page 5-9.
3-5
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
Live Video Window for MJPEG Video Streams
When the video mode is set to MJPEG, the Live Video window appears as shown in Figure 3-3.
(Depending on the camera model and camera configuration, some buttons may not be available.)
• Video Title—The video title can be configured. For more information, see the “Image settings”
section on page 5-9.
• Time—Display the current time. For more information, see the “Image settings” section on
page 5-9.
• Title and Time—Video title and time can be stamped on the streaming video. For more information,
see the “Image settings” section on page 5-9.
• Video Control Buttons—Depending on the camera model and camera configuration, some buttons
may not be available.
Figure 3-3 illustrates the live video window for MJPEG or video streams.
5 Zoom indicator.
6 Snapshot button. Click this button to capture and save still images. The captured images will be
displayed in a pop-up window. Right-click the image and choose Save Picture As to save it in
JPEG (*.jpg) or BMP (*.bmp) format.
7 Digital Zoom button. Click and uncheck “Disable digital zoom” to enable the zoom operation. The
navigation screen indicates the part of the image being magnified. To control the zoom level, drag
the slider bar. To move to a different area you want to magnify, drag the navigation screen.
8 Pause button. Pause the transmission of the streaming media. The button becomes the Resume
button after clicking the Pause button.
9 Stop button. Stop the transmission of the streaming media. Click the Resume button to continue
transmission.
10 Start MP4 Recording button. Click this button to record video clips in MP4 file format to your
computer. Press the Stop MP4 Recording button to end recording. When you exit the web
browser, video recording stops accordingly. To specify the storage destination and file name, see
the “MP4 Saving Options” procedure on page 4-2.
11 Volume button. When the Mute function is not activated, move the slider bar to adjust the volume
on the local computer.
12 Mute button. Turn off the volume on the local computer. The button becomes the Audio On button
after clicking the Mute button.
13 Talk button. Click this button to talk to people around the camera. Audio will project from the
external speaker connected to the camera. Click this button again to end talking transmission.
14 Mic Volume button. When the Mute function is not activated, move the slider bar to adjust the
microphone volume on the local computer.
15 Mute. Turn off the Mic volume on the local computer. The button becomes the Mic On button after
clicking the Mute button
16 Full Screen. Click this button to switch to full screen mode. Press the Esc key to switch back to
normal mode.

3-6
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
Figure 3-3 Live Video Window for MJPEG
1 Time. Display the current date and time. For more information, see the “Image settings” section
on page 5-9.
2 Video title. The video title can be configured. For more information, see the “Media > Image”
section on page 5-8.
3 Title and Time. Video title and time can be stamped on the streaming video. For more information,
see the “Image settings” section on page 5-9.
4 Zoom indicator.
5 Snapshot button. Click this button to capture and save still images. The captured images will be
displayed in a pop-up window. Right-click the image and choose Save Picture As to save it in JPEG
(*.jpg) or BMP (*.bmp) format.
6 Digital Zoom button: Click and uncheck “Disable digital zoom” to enable the zoom operation. The
navigation screen indicates the part of the image being magnified. To control the zoom level, drag
the slider bar. To move to a different area you want to magnify, drag the navigation screen.

3-7
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page
7 Start MP4 Recording button. Click this button to record video clips in MP4 file format to your
computer. Press the Stop MP4 Recording button to end recording. When you exit the web
browser, video recording stops accordingly. To specify the storage destination and file name, see
the “MP4 Saving Options” procedure on page 4-2.
8 Full Screen button: Click this button to switch to full screen mode. Press the Esc key to switch
back to normal mode.

3-8
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 3 IP Camera Main Page

CHAPTER
4-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
4
Client Settings
This chapter explains how to select the stream transmission mode and saving options on a local
computer. When completed with the settings on the Client Settings page, click Save on the page bottom
to enable the settings.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• H.265/H.264 Media Options, page 4-1
• H.265/H.264 Protocol Options, page 4-1
• Two Way Audio, page 4-2
• MP4 Saving Options, page 4-2
• Local Streaming Buffer Time, page 4-2
• Joystick settings, page 4-2
H.265/H.264 Media Options
Select to stream video or audio data or both. This option is enabled only when the video mode is set to
H.264 or H.265.
H.265/H.264 Protocol Options
Depending on your network environment, there are four transmission modes of H.264 or H.265
streaming:
• UDP unicast—This protocol allows for more real-time audio and video streams. However, network
packets may be lost due to network burst traffic and images may be broken. Activate UDP
connection when occasions require time-sensitive responses and the video quality is less important.
Note that each unicast client connecting to the server takes up additional bandwidth and the camera
allows up to ten simultaneous accesses.
• UDP multicast—This protocol allows multicast-enabled routers to forward network packets to all
clients requesting streaming media. This helps to reduce the network transmission load of the
camera while serving multiple clients at the same time. Note that to utilize this feature, the camera
must be configured to enable multicast streaming at the same time. For more information, see the
“RTSP Streaming” section on page 5-22.

4-2
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 4 Client Settings
Two Way Audio
• TCP—This protocol guarantees the complete delivery of streaming data and thus provides better
video quality. The downside of this protocol is that its real-time effect is not as good as that of the
UDP protocol.
• HTTP—This protocol allows the same quality as TCP protocol without needing to open specific
ports for streaming under some network environments. Users inside a firewall can utilize this
protocol to allow streaming data through.
Two Way Audio
• Half duplex—Audio is transmitted from one direction at a time, for example, from a PC holding a
web console with the camera.
• Full duplex—Audio is transmitted in both directions simultaneously.
MP4 Saving Options
You can record live video as they are watching it by clicking . Start MP4 Recording on the main
page. Here, you can specify the storage destination and file name.
• Folder—Specify a storage destination on your PC for the recorded video files. The location can be
changed.
• File name prefix—Enter the text that will be appended to the front of the video file name. A specified
folder will be automatically created on your local hard disk.
• Add date and time suffix to the file name—Select this option to append the date and time to the end
of the file name. The date and time appears in the format YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS. An example
files name is CLI_20170713_180853.
Local Streaming Buffer Time
Due to the unsteady bandwidth flow, the live streaming may lag and not be very smoothly. If you enable
this option, the live streaming will be stored temporarily on your PC’s cache memory for a few seconds
before being played on the live viewing window. This will help you see the streaming more smoothly. If
you enter 3,000 Millisecond, the streaming will delay for 3 seconds.
Joystick settings
Enable Joystick
Connect a joystick to a USB port on your management computer. Supported by the plug-in (Microsoft
DirectX), once the plug-in for the web console is loaded, it will automatically detect if there is any
joystick on the computer. The joystick should work properly without installing any other driver or
software.
Then you can begin to configure the joystick settings of connected devices.
To enable joystick settings, follow these steps:

4-3
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 4 Client Settings
Joystick settings
Step 1 Select a detected joystick, if there are multiple, from the Selected joystick menu. If your joystick is not
detected, if may be defective.
Step 2 Click Calibrate or Configure buttons to configure the joystick-related settings.
Note • If you want to assign Preset actions to your joystick, the preset locations should be configured in
advance in the Configuration > PTZ page.
• If your joystick is not working properly, it may need to be calibrated. Click the Calibrate button to
open the Game Controllers window located in Microsoft Windows control panel and follow the
instructions for trouble shooting.
• The joystick will appear in the Game Controllers list in the Windows Control panel. If you want to
check out for your devices, choose Start -> Control Panel -> Game Controllers.
Buttons Configuration
Click the Configure Buttons button and the Joystick Settings window appears.
To configure your joystick buttons, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select a button number from the Button # pull-down menu.
Tip If you are not sure of the locations of each button, use the Properties window in the Game Controllers
utility.
Step 2 Select a corresponding action, such as Patrol or Preset#.
Step 3 Click the Assign button to assign an action to the button. You can delete an association by selecting a
button number, and then click the Delete button.
Repeat the process until you are done with the configuration of all preferred actions.
The buttons you define should appear on the button list accordingly.
Step 4 Click the Save button on the Client settings page to preserver your settings.

4-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 4 Client Settings
Joystick settings

CHAPTER
5-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
5
Configuration
This chapter describes the IP camera settings options. It includes the following topics
• Accessing the Settings Pages, page 5-2
• System > General settings, page 5-3
• System > Homepage layout, page 5-3
• System > Logs, page 5-5
• System > Parameters, page 5-6
• System > Maintenance, page 5-6
• Media > Image, page 5-8
• Media > Video, page 5-14
• Media > Audio, page 5-19
• Network > General settings, page 5-19
• Network > Streaming protocols, page 5-21
• Network > QoS (Quality of Service), page 5-24
• Network > SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), page 5-25Security > User accounts,
page 5-25
• Security > User accounts, page 5-25
• Security > HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL), page 5-26
• Security > Access List, page 5-27
• Security > IEEE 802.1X, page 5-29
• Security > SSH, page 5-30
• PTZ > PTZ settings, page 5-30
• Event > Event settings, page 5-31
• Applications > Motion detection, page 5-37
• Applications > Audio detection, page 5-39
• Applications > Package management, page 5-41
• Application > PIR, page 5-41
• Recording > Recording settings, page 5-42
• Local storage > SD card management, page 5-44
5-2
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Accessing the Settings Pages
• Local storage > Content management, page 5-45
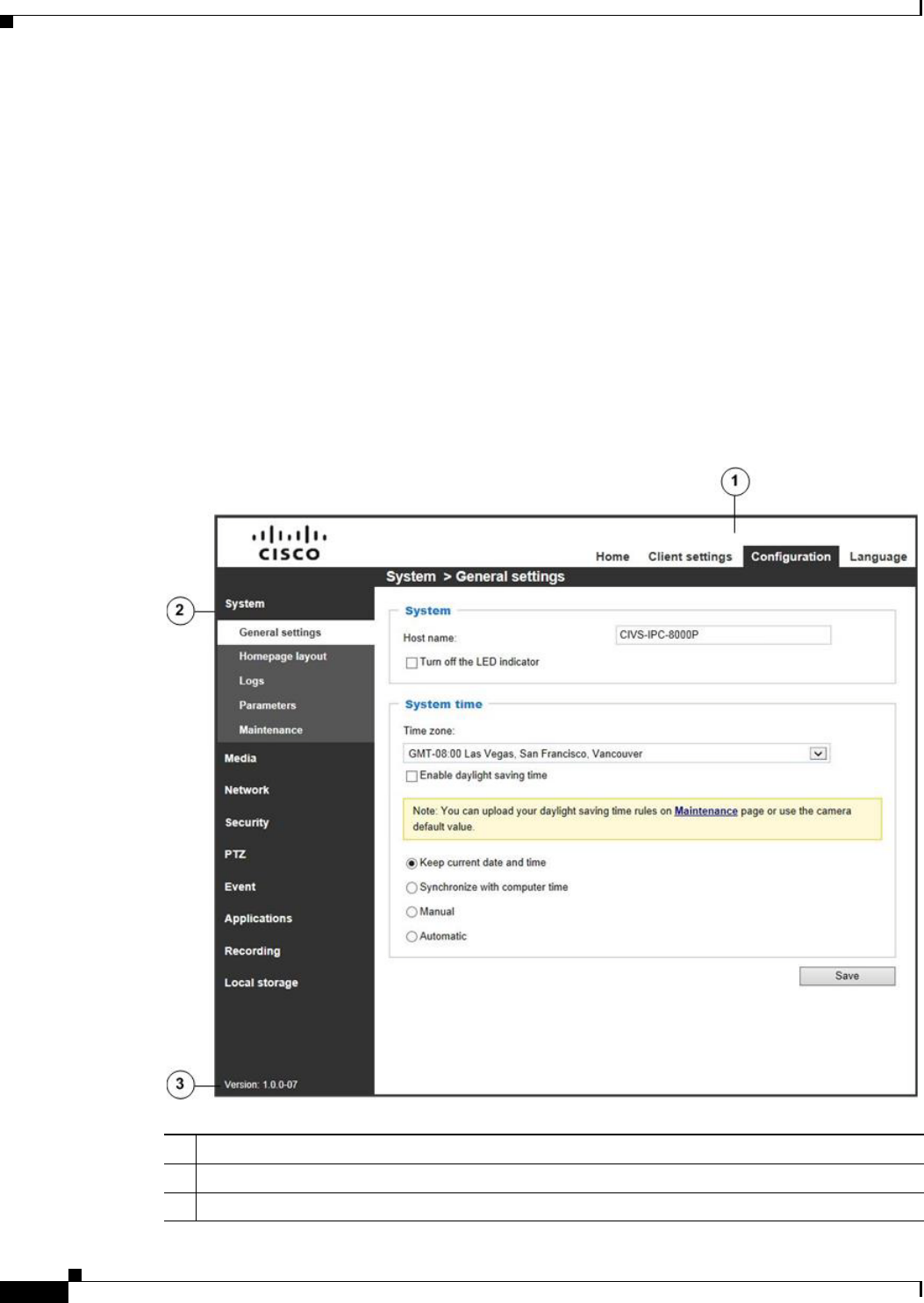
Accessing the Settings Pages
To access the settings pages, click Configuration on the main page. Only Administrators can access the
configuration page.
The camera provides an easy-to-use user interface that helps you set up the camera with minimal effort.
In order to simplify the user interface, detailed information will be hidden unless you click on the
function item. When you click on the first sub-item, the detailed information for the first sub-item will
be displayed; when you click on the second sub-item, the detailed information for the second sub-item
will be displayed and that of the first sub-item will be hidden.
Figure 5-1 illustrates the configuration main page.
Figure 5-1 Configuration Main Page
1 Navigation area.
2 Configuration list.
3 Firmware version

5-3
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
System > General settings
Each function on the configuration list will be explained in the following sections.
The Navigation Area provides access to all different views from the Home page (for live viewing),
Configuration page, and multi-language selection.
System > General settings
This section explains how to configure the basic settings for the camera, such as the host name and
system time. It is composed of the following two columns: System, and System Time. When finished
with the settings on this page, click Save at the bottom of the page to enable the settings.
• Host name—Enter a desired name for the camera. The text will be displayed at the top of the main
page.
• Turn off the LED indicators—If you do not want others to notice the camera is in operation, you can
select this option to turn off the LED indicators.
• Keep current date and time—Select this option to preserve the current date and time of the camera.
The camera internal real-time clock maintains the date and time even when the power of the system
is turned off.
• Synchronize with computer time—Select this option to synchronize the date and time of the camera
with the local computer. The read-only date and time of the PC is displayed as updated.
• Manual—The administrator can enter the date and time manually. Note that the date and time format
are [yyyy/mm/dd] and [hh:mm:ss].
• Automatic—The Network Time Protocol is a protocol which synchronizes computer clocks by
periodically querying an NTP Server.
–
NTP server—Assign the IP address or domain name of the time-server. Leaving the text box
blank connects the camera to the default time servers. The precondition is that the camera must
have the access to the Internet.
–
Update interval—Select to update the time using the NTP server on an hourly, daily, weekly, or
monthly basis.
• Time zone—Select the appropriate time zone from the list. If you want to upload Daylight Savings
Time rules, see the “Import/Export files” section on page 5-7 for details.
System > Homepage layout
This section explains how to set up your own customized homepage layout.
General settings
This column shows the settings of your home page layout. You can manually select the background and
font colors in Theme Options (the second tab on this page). The settings will be displayed automatically
in this Preview field.
• Logo graph—Here you can change the logo that is placed at the top of your homepage. To to upload
a new logo, follow these steps:
1. Click Custom and the Browse field will appear.
2. Select a logo from your files.

5-4
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
System > Homepage layout
3. Click Upload to replace the existing logo with a new one.
4. Enter a website link if necessary.
5. Click Save to enable the settings.
• Customized button—If you want to hide manual trigger buttons on the homepage, uncheck this item.
This item is checked by default.
Theme Options
Here you can change the color of your homepage layout. There are three types of preset patterns for you
to choose from. The new layout will simultaneously appear in the Preview filed. Click Save to enable
the settings.
Figure 5-2 illustrates theme options.
Figure 5-2 Theme Option
1 Font color.

5-5
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
System > Logs
To set up the custom home page, follow these steps:
Step 1 Click Custom on the left column.
Step 2 Click the field where you want to change the color on the right column.
The palette window will pop up.
Step 3 Drag the slider bar and click on the left square to select a desired color.
The selected color will be displayed in the corresponding fields and in the Preview column.
Step 4 Click Save to enable the settings.
System > Logs
This section explains how to configure the camera to send the system log to a remote server as backup.
Log server settings
To set up the remote log, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select Enable remote log.
Step 2 In the IP address text box, enter the IP address of the remote server.
Step 3 In the port text box, enter the port number of the remote server.
Step 4 When completed, click Save to enable the setting.
You can configure the camera to send the system log file to a remote server as a log backup. Before
utilizing this feature, it is suggested that the user install a log-recording tool to receive system log
messages from the camera. An example is Kiwi Syslog Daemon.
System log
The system log displays the system log in a chronological order. The system log is stored in the camera
buffer area and will be overwritten when reaching a certain limit.
2 Background color of the control area.
3 Font color of the configuration area.
4 Background color of the configuration area.
5 Preset patterns.
6 Frame color.
7 Background color of the video area.
8 Font color of the video title.

5-6
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
System > Parameters
Access log
Access log displays the access time and IP address of all viewers (including operators and
administrators) in a chronological order. The access log is stored in the camera buffer area and will be
overwritten when reaching a certain limit.
System > Parameters
The View Parameters page lists the entire system parameters. If you need technical assistance, provide
the information listed on this page.
System > Maintenance
This section explains how to restore the camera to factory default, upgrade firmware version, and so on.
General settings > Upgrade firmware
This feature allows you to upgrade the firmware of your camera. It takes a few minutes to complete the
process.
Note Do not power off the camera during the upgrade.
To upgrade the firmware, follow these steps:
Step 1 Download the latest firmware file from the Cisco website at this link:
https://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html.
The file is in .pkg file format.
Step 2 Click Browse… and locate the firmware file.
Step 3 Click Upgrade.
The camera starts to upgrade and will reboot automatically when the upgrade completes.
If the upgrade is successful, you will see “Reboot system now!! This connection will close”. After that,
access the camera again.
The following message displays when the upgrade has succeeded:
Reboot system now!!
This connection will close.
The following message is displayed when you have selected an incorrect firmware file:
Starting firmware upgrade...
Do not power down the server during the upgrade.
The server will restart automatically after the upgrade is
completed.
This will take about 1 - 5 minutes.
Wrong PKG file format
Unpack fail

5-7
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
System > Maintenance
General settings > Reboot
This feature allows you to reboot the camera, which takes about one minute to complete. When
completed, the live video page will be displayed in your browser. During the reboot process, the system
displays an information message and a a progress bar shows the status of the process
If the connection fails after rebooting, manually enter the IP address of the camera in the address field
to resume the connection.
General settings > Restore
This feature allows you to restore the camera to factory default settings.
• Network—Select this option to retain the Network Type settings (see the “Network > General
settings” section on page 5-19).
• Daylight Saving Time—Select this option to retain the Daylight Saving Time settings (see the
“Import/Export files” section on page 5-7).
• Custom Language—Select this option to retain the Custom Language settings.
• VADP—Retain the VADP modules (3rd-party software stored on the SD card) and related settings.
• Focus position—Retain the lens focus position using the previously saved position parameters.
If none of the options is selected, all settings will be restored to factory default. A status message
and progress bar is displayed during the restoring process.
Import/Export files
This feature allows you to Export / Update daylight saving time rules, custom language file,
configuration file, and server status report.
• Export daylight saving time configuration file—Click to set the start and end time of DST (Daylight
Saving).
To export, follow these steps:
1. In the Export files column, click Export to export the daylight saving time configuration file
from the camera.
2. In the File Download dialog box that pops up, click Open to review the XML file or click Save
to store the file for editing.
3. Open the file with a text editor such ac Microsoft Notepad and locate your time zone; set the
start and end time of DST.
4. When completed, save the file.
• Update daylight saving time rules—Click Browse… and specify the XML file to update.
If the incorrect date and time are assigned, you will see a warning message when uploading the file
to the camera.
The message “The file must have a .xml filename suffix” displays when attempting to upload an
incorrect file format.
• Export language file—Click to export language strings.
• Update custom language file—Click Browse... and specify your own custom language file to
upload.

5-8
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
• Export configuration file—Click to export all parameters for the device and user-defined scripts.
• Upload configuration file—Click Browse... to update a configuration file. The model and firmware
version of the device should be the same as the configuration file. If you have set up a fixed IP or
other special settings for your device, it is not suggested to update a configuration file.
• Export server status report—Click to export the current server status report, such as time, logs,
parameters, process status, memory status, file system status, network status, kernel message, and
so on.
Tip If a firmware upgrade is accidentally disrupted, say, by a power outage, you still have a last resort method
to restore normal operation. See the following for how to bring the camera back to work:
Applicable scenario:
(a) Power disconnected during firmware upgrade.
(b) Unknown reason causing abnormal LED status, and a Restore cannot recover normal working
condition.
You can use the following methods to activate the camera with its backup firmware:
(a) Press and hold down the reset button for at least one minute.
(b) Power on the camera until the Red LED blinks rapidly.
(c) After boot up, the firmware should return to the previous version before the camera hanged. (The
procedure should take 5 to 10 minutes, longer than the normal boot-up process.) When this process is
completed, the LED status should return to normal.
Media > Image
This section explains how to configure the image settings of the camera. It is composed of the following
columns: General settings, Image settings, Exposure, Lens configuration, Focus, and Privacy mask. The
Focus window is available only for models that come with motorized lens.
General settings
• Video title
–
Show_timestamp_and video_title_in_video_and_snapshots—Enter a name that will be
displayed on the title bar of the live video. A zoom indicator will be displayed on the Home page
when you zoom in/out on the live viewing window. You may zoom in/ out on the image by
scrolling the mouse wheel inside the live viewing window, and the maximum zoom in will be
up to 12.8 times.
–
Position of timestamp and video title on image—Select to display time stamp and video title on
the top or at the bottom of the video stream.
–
Timestamp and video title font size—Select the font size for the time stamp and title.
–
Video font (.ttf)—You can select a True Type font file for the display of textual messages on
video.
–
Color—Select to display color or black/white video streams.

5-9
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
–
Power line frequency—Set the power line frequency consistent with local utility settings to
eliminate image flickering associated with fluorescent lights.
–
Video orientation:
- Flip—Vertically reflect the display of the live video
- Mirror—Horizontally reflect the display of the live video. Select both options if the camera is
installed upside-down (for example, on the ceiling) to correct the image orientation. If you have
preset locations, those locations will be cleared after flip/mirror setting.
• Rotate—Indicates clockwise rotation. Rotation can be applied with flip, mirror, and physical lens
rotation settings to adapt to different mounting locations.
The camera may be installed on a vertical, side-facing, or tilted surface in order to accommodate the
interior or exterior design of a building. The interior of a building can be shaped as a narrow rectangular
space, such as corridor. The conventional HD image, such as that of a 16:9 aspect ratio, will be
incongruous with its wide horizontal view. With video rotation, the camera can more readily cover the
field of view on a tall and narrow scene.
Day/Night settings
• Switch to B/W in night mode—Select this to enable the camera to automatically switch to
Black/White during night mode.
• Turn on external IR illuminator in night mode—Select this to turn on the external IR illuminator
when the camera detects low light condition and enters the night mode. A Digital Output connection
to external IR is needed.
• IR cut filter—With a removable IR-cut filter, this camera can automatically remove the filter to let
IR light enter the light sensor during low light conditions.
–
Auto mode—The camera automatically removes the filter by judging the level of ambient light.
–
Day mode—In day mode, the camera switches on the IR cut filter at all times to block infrared
light from reaching the sensor so that the colors will not be distorted.
–
Night mode—In night mode, the camera switches off the IR cut filter at all times for the sensor
to accept infrared light, thus helping to improve low light sensitivity.
–
Synchronize with digital input—The camera automatically removes the IR cut filter when a
Digital Input is triggered. For example, the digital input can come from a housing that is
equipped with IR illumination and control circuits.
–
Schedule mode—The camera switches between day mode and night mode based on a specified
schedule. Enter the start and end time for day mode. Note that the time format is [hh:mm] and
is expressed in 24-hour clock time. By default, the start and end time of day mode are set to
07:00 and 18:00.
• Light sensor sensitivity—Tune the responsiveness of the IR filter to lighting conditions as Low,
Normal, or High.
When completed with the settings on this page, click Save to enable the settings.
Image settings
On this page, you can tune the White balance and Image adjustment.
Sensor Setting 2 are for special situations and Sensor Setting 1 is for normal situations.

5-10
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
• White balance—Adjust the value for the best color temperature.
To adjust the white balance to the best color temperature, follow these steps:.
1. Place a sheet of paper of white or cooler-color temperature color, such as blue, in front of the
lens, then allow the camera to automatically adjust the color temperature.
2. Click the On button to Fix current value and confirm the setting while the white balance is being
measured.
You may also manually tune the color temperature by pulling the RGain and BGain slide bars.
• Image Adjustment:
–
Brightness—Adjust the image brightness level, which ranges from 0% to 100%.
–
Contrast—Adjust the image contrast level, which ranges from 0% to 100%.
–
Saturation—Adjust the image saturation level, which ranges from 0% to 100%.
–
Sharpness—Adjust the image sharpness level, which ranges from 0% to 100%.
–
Gamma curve—This option is disabled when the WDR function is enabled. Adjust the image
sharpness level, which ranges from 0 to 0.45. You may let firmware Optimize your display or
select a value to change the preferred level of Gamma correction towards higher contrast or
towards the higher luminance for detailed expression for both dark and lighted areas of an
image.
• Defog—Defog helps improve the visibility quality of captured image in poor weather conditions
such as smog, fog, or smoke.
• 3D noise reduction—Adjust the 3D noise reduction strength, which ranges from Low to High.
• Enable digital image stabilizer—If you experience problems such as vibration on a pole mount, try
enable the image stabilizer.
Note All changes made to image settings is directly shown on screen. You can click Restore to recall
the original settings without incorporating the changes. When completed with the settings on
this page, click Save to enable the setting. You can also click on Profile mode to adjust all
settings above in a tabbed window for special lighting conditions.
• Enable to apply these settings at—Select the mode this profile to apply to: Day mode, Night mode,
or Schedule mode. Manually enter a range of time if you choose Schedule mode. Then check Save
to take effect.
Exposure
On this page, you can configure the Exposure measurement window, Exposure level, Exposure mode,
Exposure time, Gain control, and Day/Night mode settings. You can configure two sets of Exposure
settings: one for normal situations, the other for special situations, such as the day/night/ schedule mode.
Sensor Setting 2 are for special situations and Sensor Setting 1 is for normal situations.
• Measurement Window—This function allows you to set measurement window(s) for low light
compensation. For example, where low-light objects are posed against an extremely bright
background. You may want to exclude the bright sunlight shining through a building's corridor.
–
Full view—Calculate the full range of view and offer appropriate light compensation.
–
Custom—This option allows you to manually add customized windows as inclusive or exclusive
regions. A total of 10 windows can be configured.

5-11
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
Note The Exposure control setting in the Exposure window will be disabled when the WDR function
is enabled (system default).
The inclusive window refers to the “weighed window“; the exclusive window refers to “ignored
window“. It adopts the weighed averages method to calculate the value. The inclusive windows
have a higher priority. You can overlap these windows, and, if you place an exclusive window
within a larger inclusive window, the exclusive part of the overlapped windows will be deducted
from the inclusive window. An exposure value will then be calculated out of the remaining of
the inclusive window.
–
BLC (Back Light Compensation): This option will automatically add a “weighted region” in the
middle of the window and give the necessary light compensation.
• Exposure control:
–
Exposure level—You can manually set the Exposure level, which ranges from –2.0 to +2.0 when
WDR pro is disabled and from +0.7 to –0.7 when WDR pro is enabled (dark to bright). You can
click and drag the semi-circular pointers on the Exposure time and Gain control slide bars to
specify a range of shutter time and Gain control values within which the camera can
automatically tune to an optimal imaging result. You may prefer a shorter shutter time to better
capture moving objects, while a faster shutter reduces light and needs to be compensated by
electrical brightness gains.
–
Exposure mode—You can click and drag the semi-circular pointers on the Exposure time and
Gain control slide bars to specify a range of shutter time and Gain control values within which
the camera can automatically tune to an optimal imaging result. You can also configure the iris
size to control the amount of light. For example, you may prefer a shorter shutter time to better
capture moving objects, while a faster shutter reduces light and needs to be compensated by
electrical brightness gains.
–
Flickerless—Under some circumstances when there is a difference between the video capture
frequency and local AC power frequency (NTSC or PAL), the mismatch causes color shifts or
flickering images. If the above mismatch occurs, select the Flickerless check box, and the range
of Exposure time (the shutter time) will be limited to a range in order to match the AC power
frequency. When selected, the exposure time will be forced to stay longer than 1/120 second.
For cameras that come with fixed iris lens, setting the exposure time to longer than 1/120 second
may introduce too much lights to the lens. You can use this option to observe whether the result
of long exposure time is satisfactory.
You can click and drag the semi-circular pointers on the Exposure time and Gain control slide
bars to specify a range of shutter time and Gain control values within which the camera can
automatically tune to an optimal imaging result. For example, you may prefer a shorter shutter
time to better capture moving objects, while a faster shutter reduces light and needs to be
compensated by electrical brightness gains.
• AE Speed Adjustment—This function applies when you need to monitor fast changing lighting
conditions. For example, the camera may need to monitor a highway lane or entrance of a parking
area at night where cars passing by with their lights on can bring fast changes in light levels. The
same applies if the camera is installed on a vehicle, and when it needs to adapts to fast changes of
light when entering and leaving a tunnel.
• WDR—Refers to the Wide Dynamic Range function that enables the camera to capture details in a
high contrast environment. Use the check box to enable the function, and use the slide bar to select
the strength of the WDR Pro functionality, depending on the lighting condition at the installation
site. You can select a higher effect when the contrast is high (between the shaded area and the light
behind the objects).

5-12
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
You can click Restore to recall the original settings without incorporating the changes. When
completed with the settings on this page, click Save to enable the settings.
If you want to configure another sensor setting for day/night/schedule mode, click Profile mode to
open the Profile of exposure settings page.
–
Activated period—Select the mode this profile to apply to Night mode or the Schedule mode.
Manually enter a range of time if you select the Schedule mode. Then check the Save button for
the configuration take effect.
To set up a profile, follow these steps:
1. .Select the Profile mode tab.
2. Select the applicable mode: Night mode or Schedule mode. Manually enter a range of time if
you choose the Schedule mode.
3. Configure Exposure control settings s. See previous discussions for detailed information.
4. Click Save to enable the setting and click Close to exit the page.
Lens configuration
Reserved for future use.
Focus
Focus here refers to the Remote Focus, is applicable to cameras that are equipped with stepping motor
lens. The automated focus adjustment function eliminates the needs to physically adjust camera focus.
In an outdoor deployment consisting of a large number of cameras, the auto focus function can be very
helpful when these cameras become out of focus after days or weeks of operation. And that can easily
result from the effects of natural forces, for example, shrink and expand due to a wide range of operating
temperatures and the vibration caused by wind.
To perform the automated Focus function, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select from the bottom of the screen whether you want to perform focus adjustment on the Full view or
within a Custom focus window.
You can create a custom window and click and drag the window to a desired position on screen.
Step 2 It is recommended to Reset to the default back focus position of the sensor board.
Step 3 You can use the Open iris check box (default) to increase the iris size for a better focus adjustment result.
Step 4 Click to select the Fully-opened iris or the Full-range scan buttons.
When a full-range scan is selected, a full-range scan through the camera's entire focal length can take
about 30 to 80 seconds. If not, the auto focus scan will only go through the length where optimal focus
may occur, and that takes about 15 to 20 seconds. In theory, best results of the auto scan can be acquired
when the camera's iris is fully open.
Step 5 Wait for the scan to complete.

5-13
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Image
After a short while, the clearest image obtained should be displayed and the optimal focus range
achieved. Use the arrow marks on the sides to fine-tune the focus if you are not satisfied with the results.
You may still need to use the arrow marks to fine-tune the focus depending on the live image on your
screen. “>” means moving from wide to tele end; and “<” tele to wide.
The methodology of using the Resize Buttons at the upper left corner of the streaming window is the
same as that on the home page.
Focus Window
By default, the optimal focus is found on a full view window. You may designate a custom window
within your current field of view to acquire the best focus out of it. However, you can not place a focus
window on a distant background, for example, a hall way that stretches away for 3 meters or farther.
Doing so you will not benefit from the Focus window function.
• Full view—The focus tuning takes place by referring to the full view.
• Custom—You can create a focus window and drag it to a place of interest in your view window. It
is recommended to use this function only when you have a solid object in your view window that is
showing a consistent color or texture.
This function will not take effect if you set the focus window on a distant background. You can try
the Snapshot focus function (in Applications > Package management) when applied in the above
mentioned scenario.
Privacy Mask
Click Privacy Mask to open the settings page. On this page, you can block out sensitive zones to address
privacy concerns.
To set the privacy mask windows, follow theses:
1. Click New to add a new window.
2. You can use 4 mouse clicks to create a new masking window, which is recommended to be at
least twice the size of the object (height and width) you want to cover.
3. Enter a Window Name and click Save to enable the setting.
4. Click on the Enable privacy mask check box to enable this function.
Up to 5 privacy mask windows can be configured on the same screen.
If you want to delete the privacy mask window, click the x mark on the side of window name.

5-14
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Video
Media > Video
Stream settings—Mode - Resolution and Frame rate
For a 5MP model, the default resolution is 5 megapixels, and if bandwidth or frame rate per second is of
the concern, you can select a lower resolution while enjoying a higher frame rate (for example, in traffic
monitoring). The other configurable options is 1080P (16:9) at 60fps.
The camera supports multiple streams with frame sizes ranging from 320 x 240 to 2560 x 1920 pixels.
• Stream 1—You can define the “Region of Interest” (viewing region) and the “Output Frame Size”
(size of the live view window)
• Stream 2—The default frame size for Stream 2 is set to the 1600 x 1200
• Stream 3—The default frame size for Stream 3 is set to the 640 x 480
• Stream 4—The default frame size is 2560 x 1920, and the Viewing Window function is not available
for stream 3
Click Viewing Window to open the viewing region settings page. On this page, you can configure the
Region of Interest and the Output Frame Size for a video stream. For example, you can crop only a
portion of the image that is of your interest, and thus save the bandwidth needed to transmit the video
stream.
To set up those settings for a stream, follow these steps:
1. Select a stream for which you want to set up the viewing region.
1. Select a Region of Interest from the drop-down list. The floating frame, the same as the one in the
Global View window on the home page, will resize accordingly. If you want to set up a customized
viewing region, you can also resize and drag the floating frame to a desired position with your
mouse.
2. Choose a proper Output Frame Size from the drop-down list according to the size of your monitoring
device.
Note All the items in the “Region of Interest” should not be larger than the “Output Frame Size” (current
maximum resolution).
• The parameters of the multiple streams are as follows:
Region of Interest Output frame size
Stream 1 2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
Stream 2 2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
Stream 3 2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
2560 X 1920 ~ 320 x 240
(Selectable)
Stream 4 Fixed Fixed

5-15
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Video
When completed with the settings in the Viewing Window, click Save to enable the settings and click
Close to exit the window. The selected Output Frame Size will immediately be applied to the Frame
size of each video stream. Then you can go back to the home page to test the e-PTZ function. For
more information about the e-PTZ function, see the “PTZ > PTZ settings” section on page 5-30.
Click the stream item to display the detailed information. The maximum frame size will follow your
settings in the above Viewing Window sections.
This camera offers real-time H.265, H.264, and MJPEG compression standards (Triple Codec) for
real-time viewing. If the H.264 or H.265 mode is selected, the video is streamed via the RTSP protocol.
There are several parameters through which you can adjust the video performance:
• Frame size—You can set up different video resolutions for different viewing devices. For example,
set a smaller frame size and lower bit rate for remote viewing on mobile phones and a larger video
size and a higher bit rate for live viewing on web browsers, or recording the stream to an NVR. A
larger frame size takes up more bandwidth.
• Maximum frame rate—Limits the maximum refresh frame rate per second. Configure the frame rate
higher for smoother video viewing and for recognizing moving objects in the field of view. If the
power line frequency is set to 50Hz, the frame rates are selectable at 1fps, 2fps, 3fps, 5fps, 8fps,
12fps, 10fps, 15fps, 20fps, 24fps, and 25fps. If the power line frequency is set to 60Hz, the frame
rates are selectable at 1fps, 2fps, 3fps, 5fps, 8fps, 10fps, 12fps, 15fps, 20fps, 24fps, 25fps, and 30fps.
You can also select Customize and manually enter a value.
The frame rate will decrease if you select a higher resolution.
• Intra frame period—Determine how often for firmware to plant an I frame. The shorter the duration,
the more likely you will get better video quality, but at the cost of higher network bandwidth
consumption. Select the intra frame period from the following durations: 1/4 second, 1/2 second, 1
second, 2 seconds, 3 seconds, and 4 seconds.
• Smart Stream II
• Dynamic Intra frame period—High quality motion codecs, such as H.265, utilize the redundancies
between video frames to deliver video streams at a balance of quality and bit rate.
The encoding parameters are summarized and illustrated in Figure 5-3. The I-frames are completely
self-referential and they are largest in size. The P-frames are predicted frames. The encoder refers
to the previous I- or P-frames for redundant image information.
Figure 5-3 H.264/H.265 Frame Types
By dynamically prolonging the intervals for I-frames insertion to up to 10 seconds, the bit rates
required for streaming a video can be tremendously reduced. When streaming a video of a static
scene, the Dynamic Intra frame feature can save up to 53% of bandwidth. The amount of bandwidth
thus saved is also determined by the activities in the field of view. If activities occur in the scene,
firmware automatically shortens the I-frame insertion intervals in order to maintain image quality.
In the low light or night conditions, the sizes of P-frames tend to be enlarged due to the noises, and
hence the bandwidth saving effect is also reduced.

5-16
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Video
Streaming a typical 2MP scene normally requires 3~4Mb/s of bandwidth. With the Dynamic Intra
frame function, the bandwidth for streaming a medium-traffic scene can be reduced to 2~3Mb/s, and
during the no-traffic period of time, down to 500kb/s.
Figure 5-4 shows dynamic intra frame with static scenes. Figure 5-5 dynamic intra frame shows
activities in scenes
Figure 5-4 Dynamic Intra Frame with Static Scenes
Figure 5-5 Dynamic Intra Frame with Activities in Scenes
With the H.265 codec in an optimal scenario and when Dynamic Intra frame is combined with the
Smart Stream function, an 80% of bandwidth saving can be achieved compared with using H.264
without enabling these bandwidth-saving features.
• Smart codec—Smart codec effectively reduces the quality of the whole or the non-interested areas
on a screen and therefore reduces the bandwidth consumed.
You can manually specify the video quality for the foreground and the background areas.
Select an operation mode if Smart codec is preferred:
–
Auto tracking—The Auto mode configures the whole screen into the non-interested area. The
video quality of part of the screen returns to normal when one or more objects move in that area.
The remainder of the screen where there are no moving objects (no pixel changes) will still be
transmitted in low-quality format.
–
Manual—The Manual mode allows you to configure 3 ROI windows (Region of Interest, with
Foreground quality) on the screen. Areas not included in any ROI windows will be considered
as the non-interested areas. The details in the ROI areas will be transmitted in a higher-quality
video format.
As shown in Figure 5-6, the upper screen may contain little details of your interest, while the
sidewalk on the lower screen is included in an ROI window.

5-17
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Video
As the result, the lower screen is constantly displayed in high details, while the upper half is
transmitted using a lower-quality format. Although the upper half is transmitted using a lower
quality format, you still have an awareness of what is happening on the whole screen.
Figure 5-6 ROI Window
–
Hybrid—The major difference between the “Manual” mode and the “Hybrid” mode is that in
the “Hybrid” mode, any objects entering the non-interested area will restore the video quality
of the moving objects and the area around them. The video quality of the associated
non-interested area is immediately restored to normal to cover the moving objects. In the
“Manual” mode, the non-interested area is always transmitted using a low quality format
regardless of the activities inside.
–
Quality priority—Use the slide bar to tune the quality contrast between the ROI and
non-interested areas.
The farther the slide bar button is to the right, the higher the image quality of the ROI areas. On
the contrary, the farther the slide bar button to the left, the higher the image quality of the
non-interested area.
In this way, you may set up an ROI window as a privacy mask by covering a protected area using
an ROI window, while the remaining screen become the non-interested area. You may then
configure the non-interested area to have a high image quality, or vice versa.
You should also select the Maximum bit rate from the pull-down menu as the threshold to contain
the bandwidth consumption for both the high- and low-quality video sections in a smart stream.
• Video quality—Constant bit rate:
–
Constant bit rate—A complex scene generally produces a larger file size, meaning that higher
bandwidth will be needed for data transmission. The bandwidth utilization is configurable to
match a selected level, resulting in mutable video quality performance. The bit rates are
selectable at the following rates: 20Kbps, 30Kbps, 40Kbps, 50Kbps, 64Kbps, 128Kbps,
256Kbps, 512Kbps, 768Kbps, 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 3Mbps, 4Mbps, 6Mbps, 8Mbps, 10Mbps,
12Mbps, 14Mbps, ~ to 40Mbps. You can also select Customize and manually enter a value up
to 40Mbps.

5-18
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Video
- Target bit rate—Select a bit rate from the pull-down menu (Customized, Medium, Standard,
Good, Detailed, or Excellent). The bit rate then becomes the Average or Upper bound bit rate
number. The camera will strive to deliver video streams around or within the bit rate limitation
you impose.
- Policy—If Frame Rate Priority is selected, the camera will try to maintain the frame rate per
second performance, while the image quality will be compromised. If Image quality priority is
selected, the camera may drop some video frames in order to maintain image quality.
–
Fixed quality—On the other hand, if Fixed quality is selected, all frames are transmitted with
the same quality; bandwidth utilization is therefore unpredictable. The video quality can be
adjusted to the following settings: Medium, Standard, Good, Detailed, and Excellent. You can
also select Customize and manually enter a value.
–
Maximum bit rate—With the guaranteed image quality, you might still want to place a bit rate
limitation to control the size of video streams for bandwidth and storage concerns. The
configurable bit rate starts from 20Kbps to 40Mbps (Fixed quality).
You may also manually enter a bit rate number by selecting the Customized option.
The Maximum bit rate setting in the Fixed quality configuration can ensure a reasonable and
limited use of network bandwidth. For example, in low light conditions where a Fixed quality
setting is applied, video packet sizes can tremendously increase when noises are produced with
electrical gain.
If JPEG mode is selected, the camera sends consecutive JPEG images to the client, producing
a moving effect similar to a filmstrip. Every single JPEG image transmitted guarantees the same
image quality, which in turn comes at the expense of variable bandwidth usage. Because the
media contents are a combination of JPEG images, no audio data is transmitted to the client.
There are three parameters provided in MJPEG mode to control the video performance:
- Frame size—You can set up different video resolution for different viewing devices. For
example, set a smaller frame size and lower bit rate for remote viewing on mobile phones and
a larger video size and a higher bit rate for live viewing on web browsers. Note that a larger
frame size takes up more bandwidth.
- Maximum frame rate—Limits the maximum refresh frame rate per second. Set the frame rate
higher for smoother video quality. If the power line frequency is set to 50Hz (at the 5MP
resolution), the frame rates are selectable at 1fps, 2fps, 3fps, 5fps, 8fps, 10fps, and 12fps. If the
power line frequency is set to 60Hz, the frame rates are selectable at 1fps, 2fps, 3fps, 5fps, 8fps,
10fps, and 12fps. Up to 30 fps for JPEG with 1080P (FullHD mode). You can also select
Customize and manually enter a value. The frame rate will decrease if you select a higher
resolution.
- Video quality—The configuration method is identical to that for H.264 or H.265.
Note Video quality and fixed quality refers to the compression rate, so a lower value will produce
higher quality.
Converting high-quality video may significantly increase the CPU loading, and you may
encounter streaming disconnection or video loss while capturing a complicated scene. In the
event of occurrence, we suggest you customize a lower video resolution or reduce the frame rate
to obtain smooth video.

5-19
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Media > Audio
Media > Audio
• Mute—Select this option to disable audio transmission from the camera to all clients. That if muted,
no audio data will be transmitted even if audio transmission is enabled on the Client Settings page.
In that case, this message is displayed: “The media type has been changed to video only because the
media from server contains no audio.”
• Microphone source (8020 model only)—Select either the internal or external microphone as the
audio source.
• Internal microphone input (8020 model only)—Select the gain of the external audio input according
to ambient conditions. Adjust the gain from 0% to 100%.
• External microphone input—Select the gain of the external audio input according to ambient
conditions. Adjust the gain from 0 (least sensitive) to 100% (most sensitive).
• Audio type—Select audio codec and the sampling bit rate.
–
G.711 also provides good sound quality and requires about 64Kbps. Select pcmu (ƒÊ-Law) or
pcma (A-Law) mode.
–
G.726 is a speech codec standard covering voice transmission at rates of 16, 24, 32, and
40kbit/s.
When completed with the settings on this page, click Save to enable the settings.
Network > General settings
This section explains how to configure a wired network connection for the camera.
Network Type Tab
• LAN—Select this option when the camera is deployed on a local area network (LAN) and is
intended to be accessed by local computers. The default setting for the Network Type is LAN.
Remember to click on the Save button when you complete the Network setting.
–
Get IP address automatically—Select this option to obtain an available dynamic IP address
assigned by the DHCP server each time the camera is connected to the LAN.
–
Use fixed IP address—Select this option to manually assign a static IP address to the camera.
Enter the Static IP, Subnet mask, Default router, and Primary DNS provided by your ISP or
network administrator.
- Subnet mask—This is used to determine if the destination is in the same subnet. The default
value is “255.255.255.0”.
- Default router—This is the gateway used to forward frames to destinations in a different
subnet. Invalid router setting will disable the transmission to destinations across different
subnets.
- Primary DNS—The primary domain name server that translates host names into IP addresses.
- Secondary DNS—Secondary domain name server that backups the Primary DNS.
-Primary WINS server—The primary WINS server that maintains the database of computer
names and IP addresses.

5-20
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > General settings
- Secondary WINS server—The secondary WINS server that maintains the database of
computer names and IP addresses.
–
Enable UPnP presentation—Select this option to enable UPnP presentation for your camera so
that whenever a camera is presented to the LAN, the shortcuts to connected cameras will be
listed in My Network Places. You can click the shortcut to link to the web browser. Currently,
UPnP is supported by Windows XP or later. To utilize this feature, make sure the UPnP
component is installed on your computer.
–
Enable UPnP port forwarding—To access the camera from the Internet, select this option to
allow the camera to open ports automatically on the router so that video streams can be sent out
from a LAN. To utilize of this feature, make sure that your router supports UPnP and it is
activated.
• PPPoE (Point-to-point over Ethernet)—Select this option to configure your camera to make it
accessible from anywhere as long as there is an Internet connection. To utilize this feature, it
requires an account provided by your ISP.
To acquire your camera’s public IP address, follow these steps:
1. Set up the camera on the LAN.
2. Go to Configuration > Event > Event settings > Add server (see the “Add server” section on
page 5-33) to add a new email or FTP server.
3. Go to Configuration > Event > Event settings > Add media (see the “Add media” section on
page 5-35).
Select System log so that you will receive the system log in TXT file format that contains the
camera’s public IP address in your email or on the FTP server.
4. Go to Configuration > Network > General settings > Network type. Select PPPoE and enter
the user name and password provided by your ISP. Click Save to enable the setting.
The camera will reboot.
5. Disconnect the power to the camera; remove it from the LAN environment.
If the default ports are already used by other devices connected to the same router, the camera will
select other ports for the camera.
If UPnP is not supported by your router, you will see the following message: “Error: Router does
not support UPnP port forwarding.”
To enable the UPnP user interface on your computer, follow these steps (you must log on to the
computer as a system administrator to install the UPn components):
1. From the Start menu, click Control Panel, then click Add or Remove Programs.
2. In the Add or Remove Programs dialog box, click Add/Remove Windows Components.
3. In the Windows Components Wizard dialog box, select Networking Services and click Details.
4. In the Networking Services dialog box, select Universal Plug and Play and click OK.
5. Click Next in the following window
6. Click Finish. UPnP is enabled.
UPnP networking technology provides automatic IP configuration and dynamic discovery of devices
added to a network. Services and capabilities offered by networked devices, such as printing and file
sharing, are available among each other without the need for cumbersome network configuration. In
the case of cameras, you will see camera shortcuts under My Network Places.

5-21
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > Streaming protocols
Enabling UPnP port forwarding allows the camera to open a secondary HTTP port on the router-not
HTTP port-meaning that you have to add the secondary HTTP port number to the camera’s public
address in order to access the camera from the Internet. For example, when the HTTP port is set to
80 and the secondary HTTP port is set to 8080, the following table shows the camera’s IP address
If the PPPoE settings are incorrectly configured or the Internet access is not working, restore the
camera to factory default; see the “General settings > Restore” section on page 5-7 for details. After
the camera is reset to factory default, it will be accessible on the LAN.
• Enable IPv6—Select this option and click Save to enable IPv6 settings. This only works if your
network environment and hardware equipment support IPv6. The browser should be Microsoft
Internet Explorer 6.5, Mozilla Firefox 3.0 or above.
When IPv6 is enabled, by default, the camera will listen to router advertisements and be assigned
with a link-local IPv6 address accordingly.
–
IPv6 Information—Click this button to obtain the IPv6 information. If your IPv6 settings are
successful, the IPv6 address list will be listed in the pop-up window
To link to an IPv6 address, follow these steps:
1. Open your web browser.
2. Enter the link-global or link-local IPv6 address in the address bar of your web browser.
3. Press Enter on the keyboard or click Refresh button to refresh the web page.
If you have a secondary HTTP port (the default value is 8080), you can also link to the web page
using the following address format. (See the “HTTP streaming” section on page 5-21for
detailed information.)
http://[2001:0c08:2500:0002:0202:d1ff:fe04:65f4]/:8080
–
Manually setup the IP address: Select this option to manually set up IPv6 settings if your
network environment does not have DHCPv6 server and router advertisements-enabled routers.
If you check this item, the following blanks will be displayed for you to enter the corresponding
information:
- Optional IP address / Prefix length
- Optional Default Router
- Optional primary DNS
Network > Streaming protocols
HTTP streaming
To utilize HTTP authentication, make sure that your have set a password for the camera first; see the
“Security > User accounts” section on page 5-25 for details.
From the Internet In LAN
http://203.67.124.123:8080 http://192.168.4.160 or
http://192.168.4.160:8080

5-22
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > Streaming protocols
• Authentication—Depending on your network security requirements, the camera provides two types
of security settings for an HTTP transaction: basic and digest. If basic authentication is selected, the
password is sent in plain text format and there can be potential risks of being intercepted. If digest
authentication is selected, user credentials are encrypted using MD5 algorithm and thus provide
better protection against unauthorized accesses.
• HTTP port / Secondary HTTP port—By default, the HTTP port is set to 80 and the secondary HTTP
port is set to 8080. They can also be assigned to another port number between 1025 and 65535. If
the ports are incorrectly assigned, warning messages will be displayed:
To access the camera on the LAN, both the HTTP port and secondary HTTP port can be used to
access the camera. For example, when the HTTP port is set to 80 and the secondary HTTP port is
set to 8080, the camera’s IP address on the LAN is LAN http://192.168.4.160 or
http://192.168.4.160:8080.
• Access name for stream 1 ~ 4—This camera supports multiple streams simultaneously. The access
name is used to identify different video streams. You can click Media > Video > Stream settings to
set up the video quality of linked streams. For more information about how to set up the video
quality, see the “Stream settings—Mode - Resolution and Frame rate” section on page 5-14.
When using Mozilla Firefox to access the camera and the video mode is set to JPEG, you will receive
video comprised of continuous JPEG images. This technology, known as “server push,” allows the
camera to feed live pictures to Mozilla Firefox.
URL command: http://ip address:http port/access name for stream 1, 2, 3, 4
For example, when the Access name for stream 2 is set to video2.mjpg:
1. Launch Mozilla Firefox or Netscape.
2. Type the above URL command in the address bar. Press Enter.
3. The JPEG images will be displayed in your web browser.
Note Microsoft Internet Explorer does not support server push technology; therefore, you will not be
able to access a video stream using http://ip address:http port/access name for stream 1, 2, 3, 4.
RTSP Streaming
To utilize RTSP streaming authentication, make sure that you have set a password for controlling the
access to video stream first. See the “Security > User accounts” section on page 5-25 for details.
• Authentication—Depending on your network security requirements, the camera provides three
types of security settings for streaming via RTSP protocol: disable, basic, and digest. If basic
authentication is selected, the password is sent in plain text format, but there can be potential risks
of it being intercepted. If digest authentication is selected, user credentials are encrypted using MD5
algorithm, thus providing better protection against unauthorized access.
• Access name for stream 1 ~ 4—This camera supports multiple streams simultaneously. The access
name is used to differentiate the streaming source. If you want to use an RTSP player to access the
camera, you have to set the video mode to H.264 or H.265 and use the following RTSP URL
command to request transmission of the streaming data.
rtsp://ip address:rtsp port/access name for stream 1 to 4
For example, when the access name for stream 1 is set to live.sdp:
1. Launch an RTSP player.

5-23
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > Streaming protocols
2. Choose File > Open URL. A URL dialog box will pop up.
3. Type the above URL command in the text box.
4. The live video will be displayed in your player.
• RTSP port /RTP port for video, audio/ RTCP port for video, audio:
–
RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) controls the delivery of streaming media. By default, the
port number is set to 554.
–
The RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is used to deliver video and audio data to the clients.
By default, the RTP port for video is set to 5556.
–
The RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol) allows the camera to transmit the data by
monitoring the Internet traffic volume. By default, the RTCP port for video is set to 5557.
The ports can be changed to values through 1025 to 65535 (for RTSP port) or 1026 to 65534 for
(RTP port). The RTP port must be an even number and the RTCP port is the RTP port number plus
one, and thus is always an odd number. When the RTP port changes, the RTCP port will change
accordingly.
If the RTP ports are incorrectly assigned, the following warning message will be displayed.
Invalid port number. RTP video port must be an even number.
• Multicast settings for streams—Click the items to display the detailed configuration information.
Select the Always multicast option to enable multicast for video streams.
Unicast video transmission delivers a stream through point-to-point transmission; multicast, on the
other hand, sends a stream to the multicast group address and allows multiple clients to acquire the
stream at the same time by requesting a copy from the multicast group address. Therefore, enabling
multicast can effectively save Internet bandwith.
The ports can be changed to values between 1025 and 65535. The multicast RTP port must be an
even number and the multicast RTCP port number is the multicast RTP port number plus one, and
thus is always odd. When the multicast RTP port changes, the multicast RTCP port will change
accordingly.
If the multicast RTP video ports are incorrectly assigned, the following warning message will be
displayed:
Invalid port number. Multicast stream 1 video port must be an even number.
• Multicast TTL [1~255]—The multicast TTL (Time To Live) is the value that tells the router the
range a packet can be forwarded.
Initial TTL Scope
0 Restricted to the same host
1 Restricted to the same subnetwork
32 Restricted to the same site
64 Restricted to the same region
128 Restricted to the same continent
255 Unrestricted in scope

5-24
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > QoS (Quality of Service)
The Multicast metadata port is utilized by VADP modules to transfer video analytics results, PTZ
stream, textual data, and event messages between the camera and the client side running and
observing the video analysis. If your client side computer is located outside the local network, you
may need to open the associated TCP port on routers and firewall.
Network > QoS (Quality of Service)
Quality of Service refers to a resource reservation control mechanism, which guarantees a certain quality
to different services on the network. Quality of service guarantees are important if the network capacity
is insufficient, especially for real-time streaming multimedia applications. Quality can be defined as, for
instance, a maintained level of bit rate, low latency, no packet dropping, etc.
The following are the main benefits of a QoS-aware network:
• The ability to prioritize traffic and guarantee a certain level of performance to the data flow.
• The ability to control the amount of bandwidth each application may use, and thus provide higher
reliability and stability on the network.
Requirements for QoS
To utilize QoS in a network environment, the following requirements must be met:
• All network switches and routers in the network must include support for QoS.
• The network video devices used in the network must be QoS-enabled.
QoS models
CoS (the VLAN 802.1p model)
IEEE802.1p defines a QoS model at OSI Layer 2 (Data Link Layer), which is called CoS, Class of
Service. It adds a 3-bit value to the VLAN MAC header, which indicates the frame priority level from 0
(lowest) to 7 (highest). The priority is set up on the network switches, which then use different queuing
disciplines to forward the packets.
In the setting column for CoS, enter the VLAN ID of your switch (0~4095) and choose the priority for
each application (0~7).
If you assign Video the highest level, the switch will handle video packets first.
Note • A VLAN Switch (802.1p) is required. Web browsing may fail if the CoS setting is incorrect.
• The Class of Service technologies do not guarantee a level of service in terms of bandwidth and
delivery time; they offer a “best-effort.” You can think of CoS as “coarsely-grained” traffic control
and QoS as “finely-grained” traffic control.
• Although CoS is simple to manage, it lacks scalability and does not offer end-to-end guarantees
since it is based on L2 protocol.

5-25
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Network > SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
QoS/DSCP (the DiffServ model)
DSCP-ECN defines QoS at Layer 3 (Network Layer). The Differentiated Services (DiffServ) model is
based on packet marking and router queuing disciplines. The marking is done by adding a field to the IP
header, called the DSCP (Differentiated Services Codepoint). This is a 6-bit field that provides 64
different class IDs. It gives an indication of how a given packet is to be forwarded, known as the Per Hop
Behavior (PHB). The PHB describes a particular service level in terms of bandwidth, queueing theory,
and dropping (discarding the packet) decisions. Routers at each network node classify packets according
to their DSCP value and give them a particular forwarding treatment; for example, how much bandwidth
to reserve for it.
Use the setting options of DSCP (DiffServ Codepoint) to specify the DSCP value for each application
(0~63).
Network > SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
This section explains how to use the SNMP on the camera. The Simple Network Management Protocol
is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between
network devices. It helps network administrators to remotely manage network devices and find, solve
network problems with ease.
The SNMP consists of the following three key components:
• Manager—Network-management station (NMS), a server which executes applications that monitor
and control managed devices.
• Agent—A network-management software module on a managed device which transfers the status
of managed devices to the NMS.
• Managed device—A network node on a managed network. For example: routers, switches, bridges,
hubs, computer hosts, printers, IP telephones, cameras, web server, and database.
Before configuring SNMP settings on the this page, enable your NMS.
SNMP Configuration
• Enable SNMPv1, SNMPv2c—Select this option and enter the names of Read/Write community and
Read Only community according to your NMS settings.
• Enable SNMPv3—This option contains cryptographic security, a higher security level, which allows
you to set the Authentication password and the Encryption password.
–
Security name—According to your NMS settings, choose Read/Write or Read Only and enter
the community name.
–
Authentication type—Select MD5 or SHA as the authentication method.
–
Authentication password—Enter the password for authentication (at least 8 characters).
–
Encryption password—Enter a password for encryption (at least 8 characters).
Security > User accounts
This section explains how to enable password protection and create multiple accounts.

5-26
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Security > HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL)
Privilege Management
• PTZ control—You can modify the management privilege for operators or viewers. Select or deselect
the check boxes, then click Save to enable the settings. If you give Viewers the privilege, Operators
will also have the ability to control the camera through the main page.
• Digital Output—You can modify the management privilege for operators or viewers. Select or
deselect the check boxes, then click Save to enable the settings.
• Allow anonymous viewing—If you check this item, any client can access the live stream without
entering a User ID and Password.
Account Management
Administrators can create up to 20 user accounts.
1. Input the new user’s name and password.
2. Select the privilege level for the new user account. Click Add to enable the setting. Access rights
are sorted by user privilege (Administrator, Operator, and Viewer).
Viewers and operators can view, listen, talk to the camera, and can control DI/DO and PTZ of the
camera per the Privilege set from Privilege management. Administrator access rights can fully
control the camera operations. Only administrators can access the Configuration page.
Here you also can change a user’s access rights or delete user accounts.
1. Select an existing account to modify.
2. Make necessary changes and click Update or Delete to enable the setting.
Security > HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL)
This section explains how to enable authentication and encrypted communication over SSL (Secure
Socket Layer). It helps protect streaming data transmission over the Internet on higher security level.
Create and Install Certificate Method
Before using HTTPS for communication with the camera, a Certificate must be created first. There are
two ways: to create and install a certificate:
Method 1: Create Self-Signed Certificate
Step 1 Select this option from a pull-down menu.
Step 2 In the first column, select Enable HTTPS secure connection, then select a connection option: HTTP
& HTTPS or HTTPS only.
Step 3 Click Create certificate to generate a certificate.
The Certificate Information will automatically be displayed. You can click Certificate properties to
view detailed information about the certificate.
Step 4 Click Save to preserve your configuration, and your current session with the camera will change to the
encrypted connection.

5-27
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Security > Access List
Step 5 If your web session does not automatically change to an encrypted HTTPS session, click Home to return
to the main page. Change the URL address from “http://” to “https://” in the address bar and press Enter
on your keyboard. Some Security Alert dialogs will pop up. Click OK or Yes to enable HTTPS.
Method 2: Create and Install Certificate
Step 1 Select the option from the Method pull-down menu.
Step 2 Click Create certificate to proceed.
Step 3 Certificate information will show up in a pop-up window after clicking Create. Then click Save to
generate the certificate request.
Step 4 The Certificate request displays. If you see a “pop-up blocked” message in the bar, click OK and click
on the Information bar at the top of the page to allow pop-ups.
Step 5 Look for a trusted certificate authority, such as Symantec VeriSign Authentication Services, that issues
digital certificates. Sign in and purchase the SSL certification service. Copy the certificate request from
your request prompt and paste it in the signing request window of the CA. Proceed with the rest of the
process as CA instructions on their web page.
Step 6 Once completed, your SSL certificate should be delivered to you via an email or other means. Copy the
contents of the certificate in the email and paste it in a text/HTML/hex editor/converter, such as IDM
Computer Solution UltraEdit.
Step 7 Open a new edit, paste the certificate contents, and press ENTER at the end of the contents to add an
empty line.
Step 8 Convert file format from DOS to UNIX. Open File menu > Conversions > DOS to Unix.
Step 9 Save the edit using the “.crt” extension, using a file name like “CAcert.crt.”
Step 10 Return to the original firmware session, use the Browse button to locate the crt certificate file, and click
Upload to enable the certification.
Step 11 When the certificate file is successfully loaded, its status will be stated as Active. A certificate must have
been created and installed before you can click on the Save button for the configuration to take effect.
Step 12 To begin an encrypted HTTPS session, click Home to return to the main page. Change the URL address
from “http://” to “https://” in the address bar and press Enter on your keyboard. Some Security Alert
dialogs will pop up. Click OK or Yes to enable HTTPS.
Security > Access List
This section explains how to control access permission by verifying the client PC IP address.
General Settings
• Maximum number of concurrent streaming connection(s) limited to—Simultaneous live viewing for
1~10 clients (including stream 1 to stream 4). The default value is 10. If you modify the value and
click Save, all current connections will be disconnected and automatically attempt to re-link (IE
Explorer or Quick Time Player).

5-28
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Security > Access List
• View Information—Click this button to display the connection status window showing a list of the
current connections. Only consoles that are currently displaying live streaming will be listed in the
View Information list.
–
IP address—Current connections to the camera.
–
Elapsed time—How much time the client has been at the web page.
–
User ID—If the administrator has set a password for the web page, the clients have to enter a
user name and password to access the live video. The user name will be displayed in the User
ID column. If the administrator allows clients to link to the web page without a user name and
password, the User ID column will be empty.
–
There are some situations that allow clients access to the live video without a user name and
password:
- The administrator does not set up a root password. For more information about how to set up
a root password and manage user accounts, see the “Security > User accounts” section on
page 5-25.
- The administrator has set up a root password, but set RTSP Authentication to “disable.” For
more information about RTSP Authentication, see the “RTSP Streaming” section on page 5-22.
- The administrator has set up a root password, but allows anonymous viewing. For more
information about Allow Anonymous Viewing, see the “Privilege Management” section on
page 5-26.
–
Refresh—Click this button to refresh all current connections.
–
Add to deny list—You can select entries from the Connection Status list and add them to the
Deny List to deny access. Those checked connections will only be disconnected temporarily and
will automatically try to re-link again (IE Explore or Quick Time Player). If you want to enable
the denied list, check Enable access list filtering and click Save in the first column.
–
Disconnect—If you want to break off the current connections, select them and click this button.
Those checked connections will only be disconnected temporarily and will automatically try to
re-link again (IE Explore or Quick Time Player).
Filter
• Enable access list filtering—Check this item and click Save if you want to enable the access list
filtering function.
• Filter type—Select Allow or Deny as the filter type. If you choose Allow Type, only those clients
whose IP addresses are on the Access List can access the camera, and the others cannot. On the
contrary, if you choose Deny Type, those clients whose IP addresses are on the Access List will not
be allowed to access the camera, and the others can.
Then you can Add a rule to the following Access List. The IPv6 access list column will not be
displayed unless you enable IPv6 on the Network page. For more information about IPv6 Settings,
see the “Network > General settings” section on page 5-19 for detailed information.
There are three types of rules:
–
Single—This rule allows the user to add an IP address to the Allowed/Denied list.
–
Network—This rule allows the user to assign a network address and corresponding subnet mask
to the Allow/Deny List. The address and network mask are written in CIDR format. If IPv6 filter
is preferred, you will be prompted by the Add ipv6 filter list window. Enter the IPv6 address
and the two-digit prefix length to specify the range of IP addresses in your configuration

5-29
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Security > IEEE 802.1X
–
Range—This rule allows the user to assign a range of IP addresses to the Allow/Deny List. This
rule only applies to IPv4 addresses
Administrator IP address
• Always allow the IP address to access this device—You can check this item and add the
Administrator’s IP address in this field to make sure the Administrator can always connect to the
device.
Security > IEEE 802.1X
Enable this function if your network environment uses IEEE 802.1x, which is a port-based network
access control. The network devices, intermediary switch/access point/hub, and RADIUS server must
support and enable 802.1x settings.
The 802.1x standard is designed to enhance the security of local area networks, which provides
authentication to network devices (clients) attached to a network port (wired or wireless). If all
certificates between client and server are verified, a point-to-point connection will be enabled; if
authentication fails, access on that port will be prohibited. 802.1x utilizes an existing protocol, the
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), to facilitate communication.
The components of a protected network with 802.1x authentication include the following:
• Supplicant—A client end user (camera), which requests authentication
• Authenticator (an access point or a switch)—A “go between” that restricts unauthorized end users
from communicating with the authentication server
• 3. Authentication server (usually a RADIUS server)—Checks the client certificate and decides
whether to accept the end user access request.
Cameras support two types of EAP methods to perform authentication: EAPPEAP and EAP-TLS.
To enable 802.1x settings, follow these steps:
Step 1 Before connecting the camera to the protected network with 802.1x, apply a digital certificate from a
Certificate Authority (such as your network administrator) that can be validated by a RADIUS server.
Step 2 Connect the camera to a PC or notebook outside of the protected LAN. Open the configuration page of
the camera. Select EAP-PEAP or EAP-TLS as the EAP method. In the field, enter your ID and password
issued by the CA, then upload related certificate(s).
Step 3 When all settings are complete, move the camera to the protected LAN by connecting it to an 802.1x
enabled switch. The devices will then start the authentication automatically.
Note The authentication process for 802.1x:
1. The Certificate Authority (CA) provides the required signed certificates to the camera (the supplicant)
and the RADIUS Server (the authentication server).
2. A camera requests access to the protected LAN using 802.1X via a switch (the authenticator). The
client offers its identity and client certificate, which is then forwarded by the switch to the RADIUS

5-30
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Security > SSH
Server, which uses an algorithm to authenticate the camera and returns an acceptance or rejection back
to the switch.
3. The switch also forwards the RADIUS Server’s certificate to the camera.
4. Assuming all certificates are validated, the switch then changes the camera’s state to authorized and
is allowed access to the protected network via a preconfigured port.
Security > SSH
• Enable SSH server—Check this item to enable the SSH server.
• SSH port—Enter the SSH port that is used to access the IP camera. Valid port numbers are 22 and
1024 through 65535. The default port is 22.
Click Save to enable the settings.
PTZ > PTZ settings
This section explains how to control the camera digital e-PTZ (Pan/Tilt/Zoom) operation. Within a field
of view, it allows you to quickly move the focus to a target area for close-up viewing without physically
moving the camera.
Digital PTZ Operation (E-PTZ Operation)
The e-PTZ control settings section includes the following options. For e-PTZ related details, see the
“Patrol Settings” section on page 5-31.
• Auto pan/patrol speed—Select the speed from 1~5 (slow/fast) to set up the Auto pan/patrol speed
control.
• Zoom factor display—If you check this item, the zoom indicator will be displayed on the home page
when you zoom in/out the live viewing window.
When completed with the e-PTZ settings, click Save to enable the settings on this page.
In the Home page in the E-PTZ Mode. the e-Preset Positions will also be displayed on the home
page. Select one from the drop-down list, and the camera will move to the selected position. If you
have set up different preset positions for different streams, you can select one of the video streams
to display its separate preset positions.
• Global View—In addition to using the e-PTZ control panel, you can also use the mouse to drag or
resize the floating frame to pan/tilt/zoom the viewing region. The live view window will also move
to the viewing region accordingly.
• Moving Instantly—If you check this item, the live view window will switch to the new viewing
region instantly after you move the floating frame. If not selected, the process of moving from one
position to another will be shown.
5-31
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
• Click on Image—The e-PTZ function also supports “Click on Image“. When you click on any point
of the Global View Window or Live View Window, the viewing region will also move to that point.
That the Click on Image function only applies when you have configured a smaller “Region of
Interest” out of the maximum output frame, for example, an 800 x 600 region from out of the camera
maximum frame size.
• Patrol button—Click this button, then the camera will patrol among the selected preset positions
continuously.
Patrol Settings
You can select some preset positions for the camera to patrol.
To set up a patrol schedule, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the preset locations on the list, and click .
The selected preset locations will be displayed on the Patrol locations list.
Step 2 Set the Dwelling time for the preset location during an auto patrol.
Step 3 If you want to delete a preset location from the Patrol locations list, select it and click Remove.
Step 4 Select a location and click to rearrange the patrol order.
Step 5 Select patrol locations you want to save in the list and click Save to enable the patrol settings.
Step 6 To implement the patrol schedule, go to the Home page and click on the Patrol button.
Event > Event settings
This section explains how to configure the camera to respond to particular situations (events). A typical
application is that when a motion is detected, the camera sends buffered images to an FTP server or
e-mail address as notifications. When an event is triggered, you can specify what type of action that will
be performed. You can configure the camera to send snapshots or videos to your email address or FTP
site.
Event
To configure an event with reactive measures such as recording video or snapshots, it is necessary to
configure the server and media settings so that the camera will know what action to take (such as which
server to send the media files to) when a trigger is activated. An event is an action initiated by a
user-defined trigger source. In the Event column, click Add to open the event settings window. Here you
can arrange three elements—Schedule, Trigger, and Action—to set an event. A total of three event
settings can be configured.
• Event name—Enter a name for the event setting.
• Enable this event—Select this option to enable the event setting.
• Priority—Select the relative importance of this event (High, Normal, or Low). Events with a higher
priority setting will be executed first.

5-32
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
• Detect next event after x seconds—Enter the duration in seconds to pause motion detection after a
motion is detected. This can prevent event-related actions to take place too frequently.
Schedule
Specify the period of time during which the event trigger will take effect. Select the days of the week
and the time in a day (in 24-hr time format) for the event triggering schedule. For example, you may
prefer an event to be triggered only during the off-office hours.
Trigger
This is the cause or stimulus which defines when to trigger the camera. The trigger source can be
configured to use the camera built-in motion detection mechanism or external digital input devices.
There are several choices of trigger sources. Select the item to display the detailed configuration options.
• Video motion detection—This option makes use of the built-in motion detection mechanism as a
trigger source. To enable this function, you need to configure a Motion Detection Window first. For
more information, see the “Applications > Motion detection” section on page 5-37.
• Periodically—This option allows the camera to trigger periodically for every other defined minute.
Up to 999 minutes are allowed.
• Digital input—This option allows the camera to use an external digital input device or sensor as a
trigger source. Depending on your application, there are many choices with digital input devices on
the market which help detect changes in temperature, vibration, sound, light, etc.
• System boot—This option triggers the camera when the power to the camera is disconnected and
reconnected.
• Recording notify—This option allows the camera to trigger when the recording disk is full or when
recording starts to overwrite older data.
• Audio detection—A preset threshold can be configured with an external microphone as the trigger
to system event. The triggering condition can be an input exceeding or falling below a threshold.
Audio detection can take place as a complement to motion detection or as a method to detect
activities not covered by the camera's view.
• Camera tampering detection— This option allows the camera to trigger when the camera detects that
is being tampered with. To enable this function, you need to configure the Tampering Detection
option first. See the “Applications > Tampering detection” section on page 5-38 for detailed
information.
• Manual Triggers—This option allows you to enable event triggers manually by clicking the on/off
button on the homepage. Configure one to three associated events before using this function.
• VADP—It is presumed that you already uploaded and enabled the Cisco APP Package modules
before you can associate Cisco APP Package triggers with an Event setting.
Click on the Set VADP Trigger button to open the VADP triggers menu. The triggering conditions
available with third-party software modules known as Cisco APP Packages will be listed. Use the
arrow buttons to select these triggers. You may implant these modules for different purposes such
as triggering motion detection, or applications related to video analysis, etc. See the “Applications
> Package management” section on page 5-41 for the configuration options with Cisco App Package
modules.
Once the triggers are configured, they will be listed under the VADP option.
Action
Define the actions to be performed by the camera when a trigger is activated.

5-33
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
• Trigger digital output for x seconds—Select this option to turn on the external digital output device
when a trigger is activated. Specify the length of the trigger interval in the text box.
• Backup media if the network is disconnected—Select this option to backup media file on SD card
if the network is disconnected. This function will only be displayed after you set up a network
storage (NAS). The media to back up can include snapshot images, video, or system logs depending
on your event settings.
Add server
It is necessary to configure the server and media settings so that the camera will know what action to
take (such as which server to send the media files to) when a trigger is activated. Click Add server to
open the server setting window. You can specify where the notification messages are sent to when a
trigger is activated. A total of 5 server settings can be configured.
There are four choices of server types available: Email, FTP, HTTP, and Network storage. Select the item
to display the detailed configuration options. You can configure either one or all of them.
Server type: Email
Select to send the media files via email when a trigger is activated.
• Server name—Enter a name for the server setting.
• Sender email address—Enter the email address of the sender.
• Recipient email address—Enter the email address of the recipient.
• Server address—Enter the domain name or IP address of the email server.
• User name—Enter the user name of the email account if necessary.
• Password—Enter the password of the email account if necessary.
• Server port—The default mail server port is set to 25. You can also manually set another port.
If your SMTP server requires a secure connection (SSL), select This server requires a secure connection
(SSL).
To verify if the email settings are correctly configured, click Test. The result will be shown in a pop-up
window. If successful, you will also receive an email indicating the result.
Click Save server to enable the settings.
After you configure the first event server, the new event server will automatically display on the Server
list. If you wish to add other server options, click Add server.
Server type: FTP
Select to send the media files to an FTP server when a trigger is activated.
• Server name—Enter a name for the server setting.
• Server address—Enter the domain name or IP address of the FTP server.
• Server port—By default, the FTP server port is set to 21. It can also be assigned to another port
number between 1025 and 65535.
• User name—Enter the login name of the FTP account.
• Password—Enter the password of the FTP account.
• FTP folder name—Enter the folder where the media files will be placed. If the folder name does not
exist, the camera will automatically create one on the FTP server.

5-34
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
• Passive mode—Most firewalls do not accept new connections initiated from external requests. If the
FTP server supports passive mode, select this option to enable passive mode FTP and allow data
transmission to pass through the firewall. The firmware default has the Passive mode check box
selected.
To verify if the FTP settings are correctly configured, click Test. The result will be shown in a pop-up
window. If successful, you will also receive a test.txt file on the FTP server.
Click Save server to enable the settings.
Server type: HTTP
Select to send the media files to an HTTP server when a trigger is activated.
• Server name—Enter a name for the server setting.
• URL—Enter the URL of the HTTP server.
• User name—Enter the user name if necessary.
• Password—Enter the password if necessary.
To verify if the HTTP settings are correctly configured, click Test. The result will be shown in a pop-up
window. If successful, you will receive a test.txt file on the HTTP server.
Click Save server to enable the settings.
Network storage
Select to send the media files to a networked storage when a trigger is activated. See the “Recording >
Recording settings” section on page 42 for details. Only one NAS server can be configured. Click Save
server to enable the settings.
Action
• SD Test—Click to test your SD card. The system will display a message indicating the result as a
success or a failure. If you want to use your SD card for local storage, format it before use.
• View—Click this button to open a file list window. This function is only for SD card and Network
Storage. If you click the View button for an SD card, a Local storage page will prompt so that you
can manage the recorded files on SD card. For more information about Local storage, see the “Local
storage > SD card management” section on page 5-44. If you click the View button for a Network
storage, a file directory window will prompt for you to view recorded data on Network storage.
• Create folders by date, time, and hour automatically—If you select this item, the system will
automatically create folders by the date when video footages are stored onto the networked storage.
The following is an example of a file destination with video clips:
Click 20150120 to open the directory:

5-35
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
Add media
Click Add media to open the media setting window. You can specify the type of media that will be sent
when a trigger is activated. A total of five media settings can be configured. There are three choices of
media types available: Snapshot, Video Clip, and System log. Select the item to display the detailed
configuration options. You can configure either one or all of them.
Media type: Snapshot
Select to send snapshots when a trigger is activated.

5-36
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Event > Event settings
• Media name—Enter a name for the media setting.
• Source—Select to take snapshots from any of the video streams.
• Send x pre-event images—The camera has a buffer to temporarily hold data up to a certain limit.
Enter a number to decide how many images to capture before a trigger is activated. Up to 7 images
can be generated.
• Send x post-event images—Enter a number to decide how many images to capture after a trigger is
activated. Up to seven images can be generated. For example, if both the Send pre-event images and
Send post-event images are set to 7, a total of 15 images can be generated after a trigger is activated.
File name prefix—Enter the text that will be appended to the front of the file name.
• Add date and time suffix to the file name—Select this option to add a date/time suffix to the file
name. The date and time suffix format is YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS.
Click Save media to enable the settings.
After you set up the first media server, a new column for media server will automatically display on the
Media list. If you wish to add more media options, click Add media.
Media type: Video clip
Select to send video clips when a trigger is activated.
• Media name—Enter a name for the media setting.
• Source—Select a video stream as the source of video clip.
• Pre-event recording—The camera has a buffer to temporarily hold data up to a certain limit. Enter
a number to decide the duration of recording before a trigger is activated. Up to 9 seconds can be set.
• Maximum duration—Specify the maximum recording duration in seconds. The duration can be 1
through 20 seconds. For example, if pre-event recording is set to five seconds and the maximum
duration is set to ten seconds, the camera continues to record for another 4 seconds after a trigger is
activated.
• Maximum file size—Specify the maximum file size allowed. You may need to stitch the video clips
together when searching and packing up forensic evidence.
• File name prefix—Enter the text that will be appended to the front of the file name.
Click Save media to enable the settings.
Media type: System log
Select to send a system log when a trigger is activated.
Click Save media to enable the settings, then click Close to exit the page.
In the Event settings column, the Servers and Medias you configured will be listed; make sure the Event
-> Status is indicated as ON, in order to enable the event triggering action.
When completed, click the Save event button to enable the settings and click Close to exit Event Settings
page. The new Event / Server settings / Media will appear in the event drop-down list on the Event setting
page.
When the Event Status is ON, the event configuration above is triggered by motion detection, the camera
will automatically send snapshots via e-mail.
If you want to stop the event trigger, you can click on the ON button to turn it to OFF status or click the
Delete button to remove the event setting.
To remove a server setting from the list, select a server name from the drop-down list and click Delete.
Note that you can only delete a server setting when it is not applied in an existing event setting.

5-37
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Applications > Motion detection
To remove a media setting from the list, select a media name from the drop-down list and click Delete.
You can only delete a media setting when it is not applied in an existing event setting.
Customized Script
This function allows you to upload a sample script (.xml file) to the web page, which will save you time
on configuring the settings. There is are limited number of customized scripts you can upload; if the
current amount of customized scripts has reached the limit, an alert message will prompt.
Applications > Motion detection
This section explains how to configure the camera to enable motion detection. A total of five motion
detection windows can be configured.
To enable motion detection, follow these steps:
Step 1 Click New to add a new motion detection window.
Step 2 In the Window Name text box, enter a name for the motion detection window.
Use 4 mouse clicks to designate a detection window. You can change the window shape by dragging the
corner marks to a preferred location.
Drag the item size tab to change the minimum size of item to trigger an alarm. An item size box will
appear in the center of screen for your reference (in semi-transparent red). An intruding object must be
larger than the Item size to trigger an alarm. Change the item size according to the live view.
To delete a window, click the X mark on the right of the window name.
Step 3 Define the sensitivity to moving objects by moving the Sensitivity slide bar.
A high sensitivity is prone to produce false alarms such as the fast changes of light (such as day/night
mode switch, turning lights on/off). A movement must persist longer than 0.3 second for the motion to
be detected.
Step 4 Click Save to enable the settings.
Step 5 Select Enable motion detection to enable this function.
The Percentage Indicator will rise or fall depending on the variation between sequential images. When
motions are detected by the camera and are considered to exceed the preset threshold, the red bar rises.
Meanwhile, the motion detection window will be outlined in red.
Photos or videos can be captured instantly and configured to be sent to a remote server (via an Email or
FTP server). For more information on how to configure an event setting, see the “Event > Event settings”
section on page 5-31.
A green bar indicates that even though motions have been detected, the event has not been triggered
because the image variations still fall under the preset threshold
If you want to configure other motion detection settings for day/night/schedule mode (for example, for
a different lighting condition), click Profile to open the Motion Detection Profile Settings page. Another
three motion detection windows can be configured on this page.
To set up a profile, follow these steps:

5-38
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Applications > DI and DO
Step 1 Create a new motion detection window.
Step 2 Click the Profile mode tab.
Step 3 Select the applicable Schedule mode. Manually enter a time range.
Step 4 Click Save to enable the settings and click Close to exit the page.
This motion detection window will also be displayed on the Event Settings page. You can go to Event >
Event settings > Add Event > Trigger to select it as a trigger source. Seethe “Event > Event settings”
procedure on page 5-31 for detailed information.
How does Motion Detection Work?
There are two motion detection parameters: Sensitivity and Min. Item Size. Sensitivity is a value that
expresses the sensitivity to moving objects. A higher sensitivity setting allows camera to detect slight
movements while a lower sensitivity setting will neglect them.
The minimum item size is a threshold value that determines how many “alerted pixels” can trigger an
event. When the size of an intruding object is larger than the minimum size, and its movement persist
for 0.3 second, the motion is judged to exceed the defined threshold; and the motion window will be
outlined in red. With a large minimum item size, the size of moving object is considered as smaller than
the minimum item size, no motion alarm is triggered. With a smaller minimum item size, the same
moving object triggers the alarm.
For applications that require a high level of security management, it is suggested to use higher sensitivity
settings. However, a higher sensitivity level can also produce false alarms due to fast light changes when
switching between the day and night modes, AE switch, turning the light on or off, etc.
Applications > DI and DO
• Digital input—Select High or Low as the Normal status for the digital input. Connect the digital
input pin of the camera to an external device to detect the current connection status.
• Digital output—Select Grounded or Open to define the normal status for the digital output. Connect
the digital output pin of the camera to an external device to determine the current status.
Set up the event source as DI on Event > Event settings Add Event > Trigger. See the “Event > Event
settings” section on page 5-31 for detailed information.
Applications > Tampering detection
This section explains how to set up camera tamper detection. With tamper detection, the camera is
capable of detecting incidents such as redirection, blocking or defocusing, or even spray paint.
To set up the camera tamper detection function, follow these steps:
Step 1 Click to select the check box before tampering conditions: Tampering detection, Image too dark, Image
too bright, and Image too blurry, then enter the tamper trigger duration (10 sec. ~ 10 min.).

5-39
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Applications > Audio detection
The tamper alarm will be triggered only when the tampering factor (the difference between current frame
and pre-saved background) exceeds the trigger threshold. Conditions such as image too dark, too bright,
or too blurry (defocused) can also be configured as tampering conditions. The Trigger threshold
determines how sensitive your is tamper detection setting.
• Too bright—Shining a flashlight. The average lighting level of the scene is taken into consideration.
• Too dark—Covering the objective or spraying paint.
• Too blurry—Blurry scene can be the result of strong interference on the device, such as EMI
interference.
Step 2 You can configure Tampering Detection as a trigger element to the proactive event configurations in
Event -> Event settings -> Trigger.
For example, when the camera is tampered with, camera can be configured to send the pre- and
post-event video clips to a networked storage device. See the “Event > Event settings” section on
page 5-31 for detailed information.
Applications > Audio detection
Audio detection, along with video motion detection, is applicable in the following scenarios:
• 1. Detection of activities not covered by camera view, for example, a loud input by gun shots or
breaking a door/window.
• A usually noisy environment, such as a factory, suddenly becomes quiet due to a breakdown of
machines.
• A PTZ camera can be directed to turn to a preset point by the occurrence of audio events.
• Dark environments where video motion detection may not function well.
In the example shown in Figure 5-7, the red circles indicate where the audio alarms can be triggered
when breaching or falling below the preset threshold.

5-40
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Applications > Audio detection
Figure 5-7 Audio Detection
To configure audio detection, follow these steps:
Step 1 Once the Audio detection window is opened, the current sound input will be interactively indicated by
a fluctuating yellow wave diagram.
Step 2 Use a mouse click to drag the Alarm level tab to a preferred location on the slide bar.
Step 3 Select the Enable audio detection check box and click Save to enable the feature.
Note • The volume numbers (0~100) on the side of wave diagram does not represent decibel (dB). Sound
intensity level has already been mapped to preset values. You can, however, use the real-world inputs
at your installation site that are shown on the wave diagram to configure an alarm level.
• To configure this feature, you must not mute the audio in Configuration > Media > Audio. The
default of the camera can be muted due to the lack of an internal microphone. An external
microphone is provided by users.
You can use the Profile window to configure a different Audio detection setting. For example, a place
can be noisy in the day time and become very quiet in the night. To make this configuration, follow these
steps:
Step 1 Click on the Enable this profile check box.
Once the Audio detection window is opened, the current sound input will be interactively indicated by
a fluctuating yellow wave diagram.

5-41
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Applications > Package management
Step 2 Use a mouse click to drag the Alarm level tab to a preferred location on the slide bar.
Step 3 Select the Day, Night, or Schedule mode check circles.
You may also manually configure a period of time during which this profile will take effect.
Step 4 Click Save and then click Close to complete your configuration.
If the Alarm level and the received volume are set within a range of 20% on the wave diagram, frequent
alarms will be triggered. It is recommended to set the Alarm level farther apart from the detected sound
level.
To configure and enable this feature, you must not configure video stream #1 into Motion JPEG. If an
external microphone input is connected and recording of audio stream is preferred, audio stream is
transmitted between camera and viewer/recording station along with stream #1.
See the “Media > Audio” section on page 5-19 for audio settings and the “Media > Video” section on
page 5-14 for video streaming settings.
Applications > Package management
You can store and execute Cisco or 3rd-party software modules onto the camera's flash memory or SD
card. These software modules can apply in video analysis for intelligent video applications such as
license plate recognition, object counting, or as an agent for edge recording, etc.
• Once the software package is successfully uploaded, the module configuration (vadp. xml)
information is displayed. When uploading a module, the camera will examine whether the module
fits the predefined Cisco APP package requirements. Contact Cisco or the vendor of your 3rd-party
module for the parameters contained within.
• You can also run Cisco APP package packages as a means to access updated functionality instead
of replacing the entire firmware.
• For some cameras the flash is too small to hold Cisco APP package packages. These cameras will
have its Save to SD card check box selected and grayed-out for all time.
• The file system of SD card (FAT32) does not support soft (symbolic) link. It will return failure if
your module tries to create soft links on SD card.
To utilize a software module, acquire the software package and click Browse and Upload buttons.
To start a module, select the radio button in front, and click the Start button.
If you should need to remove a module, select the radio button in front and then click the Stop button.
By then the module status will become OFF, and the X button will appear at the end of the row. Click on
the X button to remove an existing module.
When prompted by a confirm message, click Yes to proceed.
That the actual memory consumed while operating the module will be indicated on the Memory status
field. This helps determine whether a running module has consumed too much of system resources.
Application > PIR
Click the check box to enable the PIR detection. Default is disabled.

5-42
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Recording > Recording settings
Recording > Recording settings
This section explains how to configure the recording settings for the camera.
Recording Settings
Insert your SD card and click SD test to test
Note Remember to format your SD card via the camera’s web console (in the Local storage SD card
management page) when using it for the first time. See the “Local storage > SD card management”
section on page 5-44 for detailed information.
Click Add to open the recording setting window. On this page, you can define the adaptive recording,
recording source, recording schedule, and recording capacity. A total of 2 recording settings can be
configured.
• Recording name—Enter a name for the recording setting.
• Enable this recording—Select this option to enable video recording.
• With adaptive recording—Select this option will activate the frame rate control according to alarm
trigger. The frame control means that when there is a triggered alarm, the frame rate will raise up to
the value you configured on the Video quality page. See the “Media > Video” section on page 5-14
for more information.
If you enable adaptive recording on a camera, only when an event is triggered on Camera A will the
server record the full frame rate streaming data; otherwise, it will only request the I frame data
during normal monitoring, thus effectively saves bandwidths and storage space.
Note To enable adaptive recording, make sure you have set up the trigger source such as Motion
Detection, DI Device, or Manual Trigger.
When there is no alarm trigger:
- JPEG mode: record 1 frame per second
- H.264 or H.265 mode: record the I frame only
When the I frame period is >1s on Video settings page, firmware will force decrease the I frame
period to 1s when adaptive recording is enabled.
The alarm trigger includes: motion detection and DI detection. See the “Event > Event settings”
section on page 5-31.
–
Pre-event recording and post-event recording—The camera has a buffer that temporarily holds
data for a period of time. Therefore, when an event occurs, the camera can retrieve image frames
taken several seconds ago. Enter a number to define the duration of recording before and after
a trigger is activated.
• Priority—Select the relative importance of this recording (High, Normal, or Low). Recording with
a higher priority setting will be executed first.
• Source—Select a video stream as the recording source.
To enable recording notification configure Event settings first. See the “Event > Event settings” section
on page 5-31.

5-43
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Recording > Recording settings
Follow these steps to set up recording:
1. Trigger: Select a trigger source.
–
Schedule—The server will start to record files on the local storage or network storage (NAS).
–
Network fail—Since network fail, the server will start to record files on the local storage (SD
card).
2. Destination: You can select the SD card or network storage (NAS) for the recorded video files. If
you have not configured a NAS server, see the following steps.
NAS server
1. Click Add NAS server to open the server setting window.
2. Fill in the information for your server.
–
In the Network storage location field, enter the network storage path in the format
\\server_name or IP_address\folder_name
–
In the Username and password field, enter information for your server
3. Click Test to check the setting. The result will be shown in a pop-up window. If successful, you will
receive a test.txt file on the network storage server.
4. Enter a server name.
5. Click Save to complete the settings and click Close to exit the page.
• Capacity—You can choose either the entire free space available or limit the reserved space. The
recording size limitation must be larger than the reserved amount for cyclic recording.
• Enable cyclic recording—If you check this item, when the maximum capacity is reached, the oldest
file will be overwritten by the latest one. The reserved amount is reserved for the transaction stage
when the storage space is about to be full and new data arrives. The minimum for the Reserved space
must be larger than 15 MB.
• Recording file management—You can manually assign the Maximum duration and the Maximum
file size for each recording footage. You may need to stitch individual files together under some
circumstances. You may also designate a file name prefix by filling in the responsive text field.
• File name prefix—Enter the text that will be appended to the front of the file name.
If you want to enable recording notification, click Event to configure event triggering settings. See
the “Event > Event settings” section on page 5-31 for more details.
When completed, select Enable this recording. Click Save to enable the setting and click Close to
exit this page. When the system begins recording, it will send the recorded files to the network
storage. The new recording name will appear in the drop-down list on the recording page.
To remove a recording setting from the list, select a recording name from the drop-down list and
click Delete.

5-44
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Local storage > SD card management
• Click recording (Name)—Opens the Recording Settings page to modify.
• Click ON (Status)—The Status will become OFF and stop recording.
• Click NAS (Destination)—Opens the file list of recordings. For more information about folder
naming rules, see the “Add server” section on page 5-33.
Local storage > SD card management
Note • It is recommended to turn OFF the recording activity before you remove an SD card from the
camera.
• The lifespan of an SD card is limited. Regular replacement of the SD card can be necessary.
• Camera file system takes up several megabytes of memory space. The storage space cannot be used
for recording.
• An SD card that already contains data recorded by another device should not be used in this camera.
• Do not modify or change the folder names in the SD card. That may result in camera malfunctions.
This section explains how to manage the local storage on the camera. Here you can view SD card status,
and implement SD card control.
SD card status
This column shows the status and reserved space of your SD card. Remember to format the SD card when
using for the first time. If the SD card status field shows “Detached,” there is no SD card.
SD card format
The SD card format FAT32 or Ext4 is applied to SD cards up to 32GB. For SD cards larger 32GB, only
the Ext4 file format is applied. If EXT4 is applied, the computers running Windows will not be able to
access the contents on the SD card unless using some 3rd-party software.
SD card control
• Enable cyclic storage—Check this item if you want to enable cyclic recording. When the maximum
capacity is reached, the oldest file will be overwritten by the latest one.
• Enable automatic disk cleanup—Check this item and enter the number of days you wish to retain a
file. For example, if you enter “7 days,” the recorded files will be stored on the SD card for 7 days.
Click Save to enable your settings.

5-45
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Local storage > Content management
Local storage > Content management
This section explains how to manage the content of recorded videos on the camera. Here you can search
and view the records and view the searched results.
Searching and Viewing the Records
This column allows the user to set up search criteria for recorded data. If you do not select any criteria
and click Search button, all recorded data will be listed in the Search Results column.
• File attributes—Select one or more items as your search criteria.
• Trigger time—Manually enter the time range you want to search for contents created at a specific
point in time.
Click Search and the recorded data corresponding to the search criteria will be listed in Search Results
window.
Search Results
The Search results window includes four columns: Trigger time, Media type, Trigger type, and Locked.
From the drop-down list at the bottom left, choose the number of entries to be displayed on one page.
• Play—Click on a search result which will highlight the selected item. A Play window will appear
on top for immediate review of the selected file.
• Download—Click on a search result to highlight the selected item in purple. Then click the
Download button and a file download window will pop up for you to save the file.
• JPEGs to AVI—This functions only applies to JPEG format files such as snapshots. You can select
several snapshots from the list, then click this button. Those snapshots will be converted into an AVI
file.
• Lock/Unlock—Select the check box in front of a desired search result, then click this button. The
selected items will become Locked, which will not be deleted during cyclic recording. You can click
again to unlock the selections.
• Remove—Select the desired search results, then click this button to delete the files.

5-46
Cisco Video Surveillance 8020/8030 IP Camera Reference Guide
Chapter 5 Configuration
Local storage > Content management


